How to change virtual memory size on Windows 10
If your PC runs low on virtual memory, you can adjust the size using Settings and Command Prompt.
On Windows 10, virtual memory (or paging file) is an essential component (hidden file) designed to remove and temporarily store less frequently used modified pages allocated in RAM (Random-Access Memory) to the hard drive. Using this approach lets the system prioritize faster physical memory for more frequent processes and apps, improving the overall performance and preventing the computer from locking up in the event it runs out of system memory.
In addition, the paging file is important to support crash dumps during a system crash (Blue Screen of Death), as without a large enough page file, a dump with all the contents of the system memory won't be created.
Although the system can manage the paging file size automatically according to various factors, sometimes, you may still need to increase the default virtual memory values manually. For example, when you see the "Your system is low on virtual memory" message. You're noticing slow performance over time, or a particular application requires specific parameters to work correctly.
If the computer has issues with virtual memory, the device doesn't have enough memory, or you're trying to improve the system performance, Windows 10 includes the settings to increase the size of the virtual memory in at least two ways using the Settings app and Command Prompt.
In this how-to guide, I will walk you through the steps to increase the size of the virtual memory to improve Windows 10 responsiveness.
Warning: Although anyone can change the paging file size, using these instructions is only recommended if you have a valid reason and know what you're doing.
How to increase virtual memory form Settings
To adjust the virtual memory size on Windows 10, use these steps:
Get the Windows Central Newsletter
All the latest news, reviews, and guides for Windows and Xbox diehards.
- Open Settings.
- Click on System.
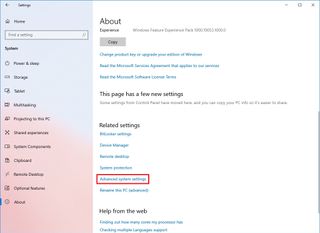
- Click on About.
- Click the "Advanced system settings" option under the "Related settings" section.
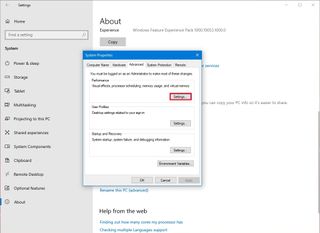
- Click the Advanced tab.
- Click the Settings button under the "Performance" section.
- Click the Advanced tab.
- Click the Change button under the "Virtual memory" section.
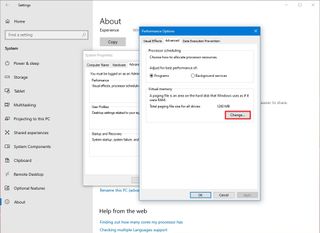
- Clear the "Automatically manage paging files size for all drives" option.
- Select the Custom size option.
- Specify the initial and maximum size for the paging file in megabytes.
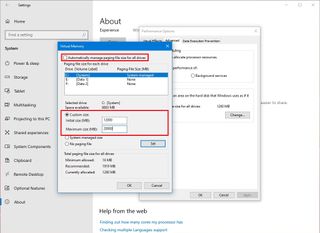
- Quick tip: The virtual memory size is unique to each device and can't be generalized. However, usually, it's recommended to use a number that's one and a half times the total available memory for the "Initial size" and three times the available memory for the "Maximum size" when possible. You also have to make sure that the device has enough free space to store the new page file.
- Click the Set button.
- Click the OK button.
- Click the OK button again.
- Restart your device.
Once you complete the steps, you should notice an increase in performance when navigating Windows 10 as well as when running multiple apps at the same time.
If you need to revert the changes, you can use the same instructions, but on step 10, check the "Automatically manage paging size for all drives" option and restart your device.
How to increase virtual memory from Command Prompt
To modify the paging file size with Command Prompt, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Command Prompt, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
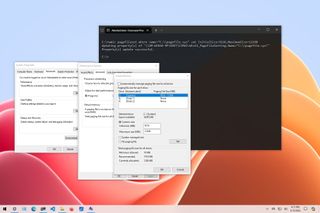
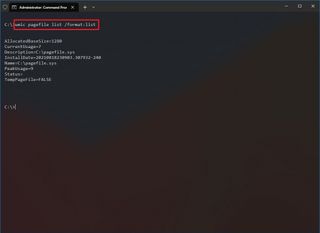
- Type the following command to understand the current status of the paging file and press Enter: wmic pagefile list /format:list
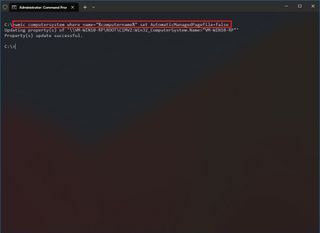
- Type the following command to switch from manage to custom virtual memory and press Enter: wmic computersystem where name="%computername%" set AutomaticManagedPagefile=false
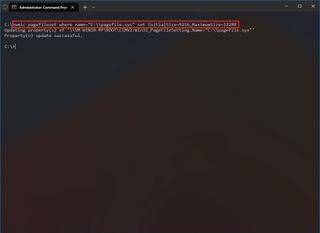
- Type the following command to set the initial and maximum size of the virtual memory and press Enter: wmic pagefileset where name="C:\\pagefile.sys" set InitialSize=YOUR-INIT-SIZE,MaximumSize=YOUR-MAX-SIZE
This example sets the paging file to "9216" and "12288" megabytes for the initial and maxium size: wmic pagefileset where name="C:\\pagefile.sys" set InitialSize=9216,MaximumSize=12288
- Type the following command to restart your computer and press Enter: shutdown -r -t 00
After you complete the steps, the device will start using the new values for virtual memory, which, if done correctly, should help to improve system performance.
If you no longer need to use the custom size for virtual memory, you can always revert the changes and allow Windows 10 to manage this feature using this command: wmic computersystem where name="%computername%" set AutomaticManagedPagefile=true and restart the computer.
While it's recommended to use one and a half times the available memory for the initial and three times the memory for the maximum size, make sure to test the changes and adjust the values if you're experiencing freezes, crashes, and other problems.
Although it's possible to disable virtual memory on Windows 10, even when you have a large amount of system memory, it's not recommended to disable this feature. Usually, if you disable paging file, some applications may stop working, some system features may not work efficiently, and you may end up with some weird behaviors.
More resources
For more helpful articles, coverage, and answers to common questions about Windows 10 and Windows 11, visit the following resources:
Mauro Huculak is technical writer for WindowsCentral.com. His primary focus is to write comprehensive how-tos to help users get the most out of Windows 10 and its many related technologies. He has an IT background with professional certifications from Microsoft, Cisco, and CompTIA, and he's a recognized member of the Microsoft MVP community.

