NVIDIA adds support for OpenAI's Chat API to its latest GPUs. Here's why it's it's a big deal.
During Microsoft's Ignite conference, NVIDIA announced updates to TensorRT-LLM.
All the latest news, reviews, and guides for Windows and Xbox diehards.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
What you need to know
- TensorRT-LLM is adding OpenAI's Chat API support for desktops and laptops with RTX GPUs starting at 8GB of VRAM.
- Users can process LLM queries faster and locally without uploading datasets to the cloud.
- NVIDIA pairs this with "Retrieval-Augmented Generation" (RAG), allowing more bespoke LLM use cases.
During Microsoft's Ignite conference today, NVIDIA announced an update to their TensorRT-LLM, which launched in October. The main announcements today are that the TensorRT-LLM feature is now gaining support for LLM APIs, specifically OpenAI Chat API, which is the most well-known at this point, and also that they have worked to improve performance with TensorRT-LLM to get better performance per token on their GPUs.
There is a tertiary announcement that is quite interesting also. NVIDIA is going to include Retrieval-Augmented Generation with the TensorRT-LLM. This allows an LLM to use an external data source for its knowledge base rather than relying on anything online—a highly demanded feature for AI.
What is TensorRT-LLM?
- Microsoft is making its own Arm chips
- Copilot comes to all of Microsoft 365
- Bing Chat rebranded to Copilot
- Microsoft Loop now generally available
- Microsoft Mesh and Immersive Spaces
- Microsoft Planner merges To Do and Project
- Microsoft launches Copilot Studio
- Microsoft Security Copilot
- Copilot web app goes live
NVIDIA recently rolled out NVIDIA TensorRT-LLM, an open-source library that allows for local computing of LLMs on NVIDIA hardware. NVIDIA touts this to gain privacy and efficiency when dealing with large datasets or private information. Whether that information is sent through an API like OpenAI's Chat API is secure. You can learn more about NVIDIA TensorRT-LLM at NVIDIA's developer site.
The changes announced today to NVIDIA TensorRT-LLM are the addition of OpenAI's Chat API and performance improvements for previously supported LLMs and AI models like Llama 2 and Stable Diffusion through DirectML enhancements.
This technology and computing can be done locally through NVIDIA's AI Workbench. This "unified, easy-to-use toolkit allows developers to quickly create, test, and customize pre-trained generative AI models and LLMs on a PC or workstation." NVIDIA has an early access sign-up page for those interested in using it.
NVIDIA TensorRT-LLM is an open-source library that accelerates and optimizes inference performance of the latest large language models (LLMs) on the NVIDIA AI platform
NVIDIA
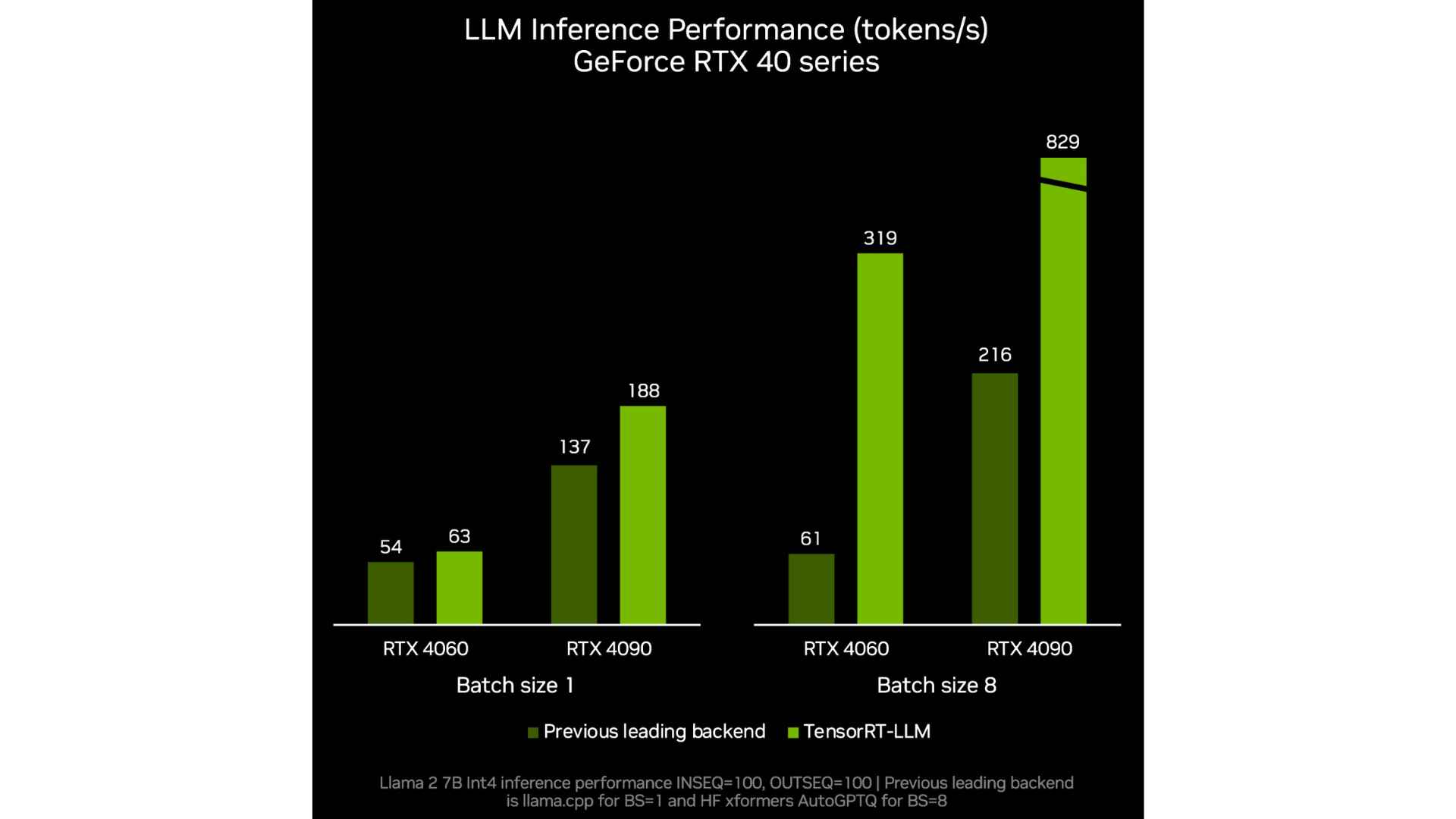
Nvidia is also showing an improvement to per token performance for LLMs as we can see in these in-house NVIDIA benchmarks. As always, be wary of manufacturer benchmarks and testing for accurate reporting of performance gain.
Now that we know NVIDIA's TensorRT-LLM, why is this special or useful? For the most part, running locally on an NVIDIA-powered workstation or PC will likely result in the same answers to queries, albeit likely at a slower pace due to the lack of cloud computing power.
All the latest news, reviews, and guides for Windows and Xbox diehards.
NVIDIA's picture for this use case comes together when discussing the other announcement today from NVIDIA, namely the integration with a new technology or feature called Retrieval-Augmented Generation.
What is Retrieval-Augmented Generation
The term retrieval-augmented generation was coined in a paper by a series of authors, with the lead author being Patrick Lewis. It is the name being adopted by the industry for a solution to a problem everybody who has used an LLM has encountered. Out-of-date or information that is correct but erroneous in the context of the discussion. The in-depth details of how RAG works can be found in one of NVIDIA's Technical Briefs.
Retrieval-augmented generation is a technique for enhancing the accuracy and reliability of generative AI models with facts fetched from external sources.
Rick Merritt
By pairing retrieval-augmented generation with NVIDIA's TensorRT-LLM, end users can customize what information the LLM has access to when it runs its queries. ChatGPT recently announced custom GPTs that could offer similar results.
As was discussed in our article around custom GPTs, the ability to make bespoke, single-purpose LLM instances with either a custom GPT or, in this case, an LLM instance that, using retrieval-augmented generation, only has access to all of the published works of Charles Dickens and nothing else, could assist in creating purpose-built, meaningful and accurate LLMs for different use cases.
Will TensorRT-LLM be useful?
What does this all mean together? There are some real opportunities for this to be used meaningfully. How easy will it be to implement, or how safe will the data be? Only time will tell. There is potential here for AI improvements, especially at an enterprise level, to improve workflows, offer more convenient access to complicated information, and assist employees with challenging tasks.
Even though these tasks will be run locally, they will still go through the normal LLM APIs, which will face the same content restrictions and limitations they do now. However, as technologies like NVIDIA's TensorRT-LLM make it faster to use an LLM offline, somebody could integrate it with something like EvilGPT, which has no limitations on its conduct and is currently being used to craft malware and assist in cyber attacks, the potential for an AI performing some real damage only amplifies.
What do you think about NVIDIA's updates to TensorRT-LLM? Can you think of any uses for it that I missed? Let us know in the comments.

Colton is a seasoned cybersecurity professional that wants to share his love of technology with the Windows Central audience. When he isn’t assisting in defending companies from the newest zero-days or sharing his thoughts through his articles, he loves to spend time with his family and play video games on PC and Xbox. Colton focuses on buying guides, PCs, and devices and is always happy to have a conversation about emerging tech and gaming news.
