I always make these 9 tweaks in Windows Terminal for a more readable and consistent experience on Windows 11 — and they're for more than just aesthetics
Check out my tweaks that make the Terminal more readable, consistent, and productive across all the command-line tools.
All the latest news, reviews, and guides for Windows and Xbox diehards.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Windows Terminal is the new shell for all your command-line tools, including PowerShell, Command Prompt, and Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL). However, out of the box, it is not configured to meet everyone's preferences. Every time I set up a new Windows 11 installation on an existing or new computer, I apply a specific set of configurations before doing any real work.
These changes are not about aesthetics alone. They improve readability, reduce friction when switching between shells, and make the Terminal behave consistently across machines. Whether you use PowerShell, Command Prompt, WSL, or all three, these settings turn Windows Terminal from a good default app into a tool that actually looks and works the way you want.
In this how-to guide, I will walk through the exact Windows Terminal configuration I always use on Windows 11.
These are my personal recommendations and the settings I use every day. This list does not cover every customization available in Windows Terminal. You can apply one, several, or all of these changes depending on your workflow and preferences.
My essential customization tweaks for Windows Terminal
Windows Terminal is highly customizable, and the settings I’m highlighting here reflect my personal configuration. They’re not presented in any particular order, but each one plays a role in making the Terminal more efficient and consistent for daily use.
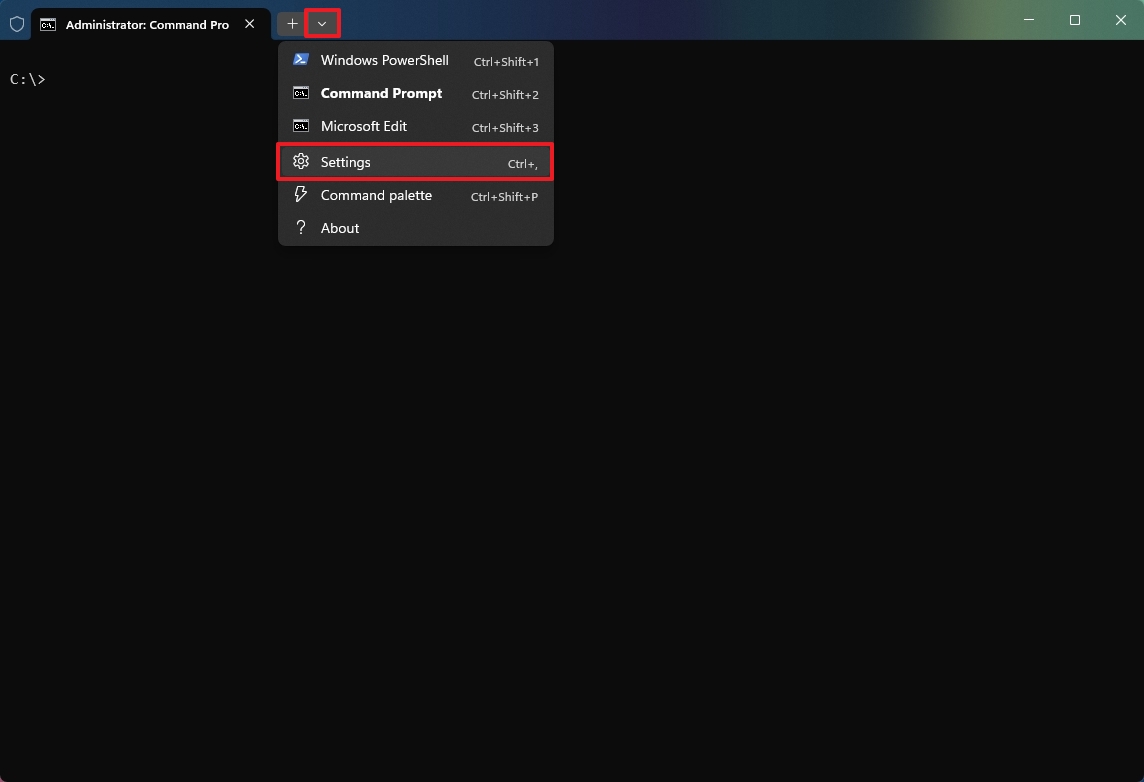
1. Set Command Prompt as the default startup profile
Although PowerShell may be the preferred default and preferred shell, I always end up opening Command Prompt. As a result, I always set startup settings to launch Command Prompt.
To set Command Prompt as the default command-line experience, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Windows Terminal and click the top result to open the app.
- Click the main menu and choose the Settings (Ctrl+,) option.
- Click on Startup.
- Select the Command Prompt option in the "Default profile" setting.
- Click the Save button.
Once you complete the steps, every time you open the Terminal, the Command Prompt shell will open instead of PowerShell.
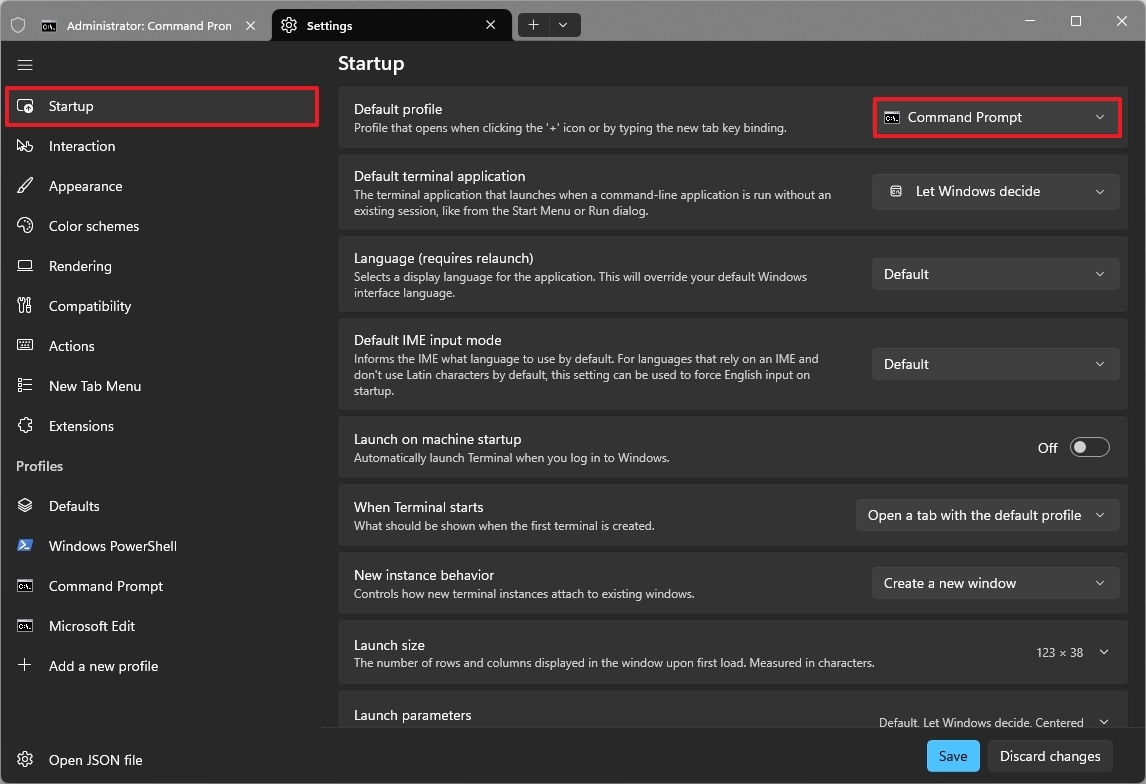
2. Choose a global starting directory for every shell
If you often find yourself switching to the same directory when opening the Windows Terminal, you can specify the location where the command-line utility should initialize during startup.
To start the Windows Terminal in a specific folder location, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Windows Terminal and click the top result to open the app.
- Click the main menu and choose the Settings (Ctrl+,) option.
- Click on Defaults.
- Click the Starting directory setting.
- Click the Browse button.
- Select the starting directory, such as C:\.
- Click the Select Folder button.
- Click the Save button.
After you complete the steps, whether you open the Terminal in Command Prompt or PowerShell, the command-line shell will start in the specified directory.
3. Remove unused and duplicate Terminal profiles
Microsoft ships the Terminal with different profiles that you probably never use, including the Azure Cloud Shell and a second PowerShell profile corresponding to version 7.x, not the legacy version, which is known as "Windows PowerShell." If you want to declutter the experience, it's possible to delete any profile you may not use.
To delete unnecessary profiles, use the steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Windows Terminal and click the top result to open the app.
- Click the main menu and choose the Settings (Ctrl+,) option.
- Click the Azure Cloud Shell profile under the "Profiles" section (if applicable).
- Click the Delete profile button.
- Click the PowerShell profile under the "Profiles" section (if applicable).
- Quick note: This entry is for the new version of PowerShell, not the legacy "Windows PowerShell". If you have the entry for the legacy version, don't delete it.
- Click the Delete profile button.
Once you complete the steps, you may need to repeat the instructions to remove other profiles you're not using.
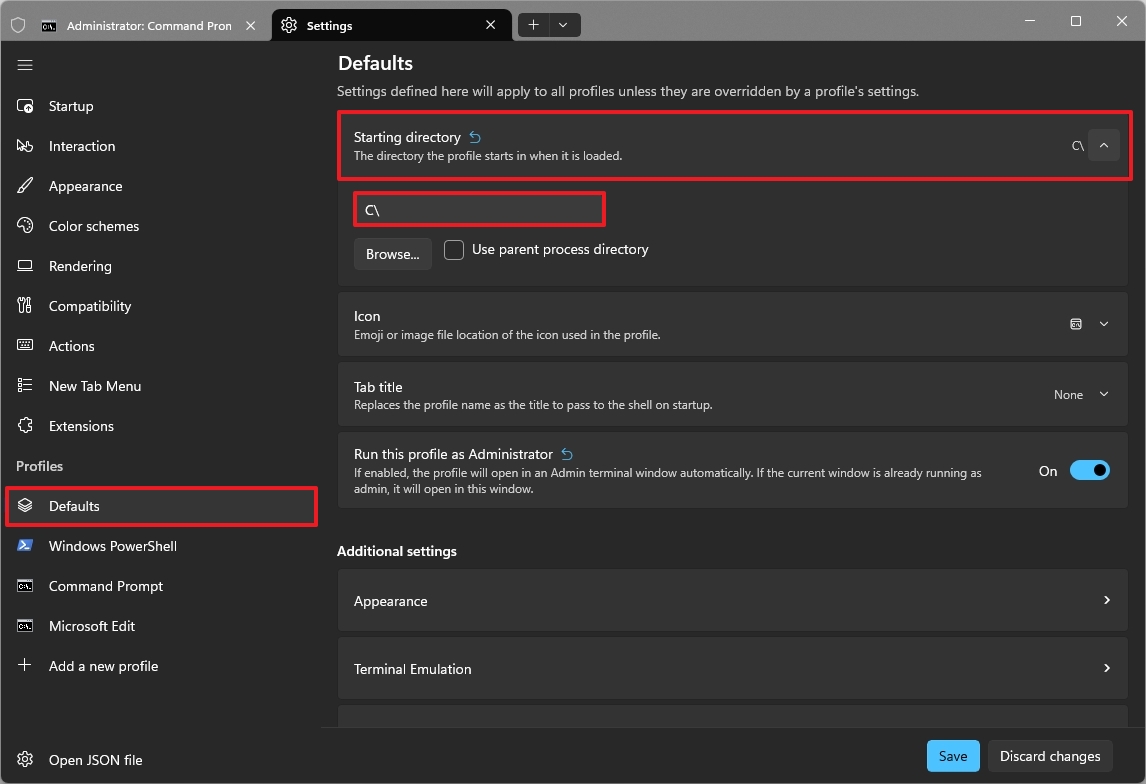
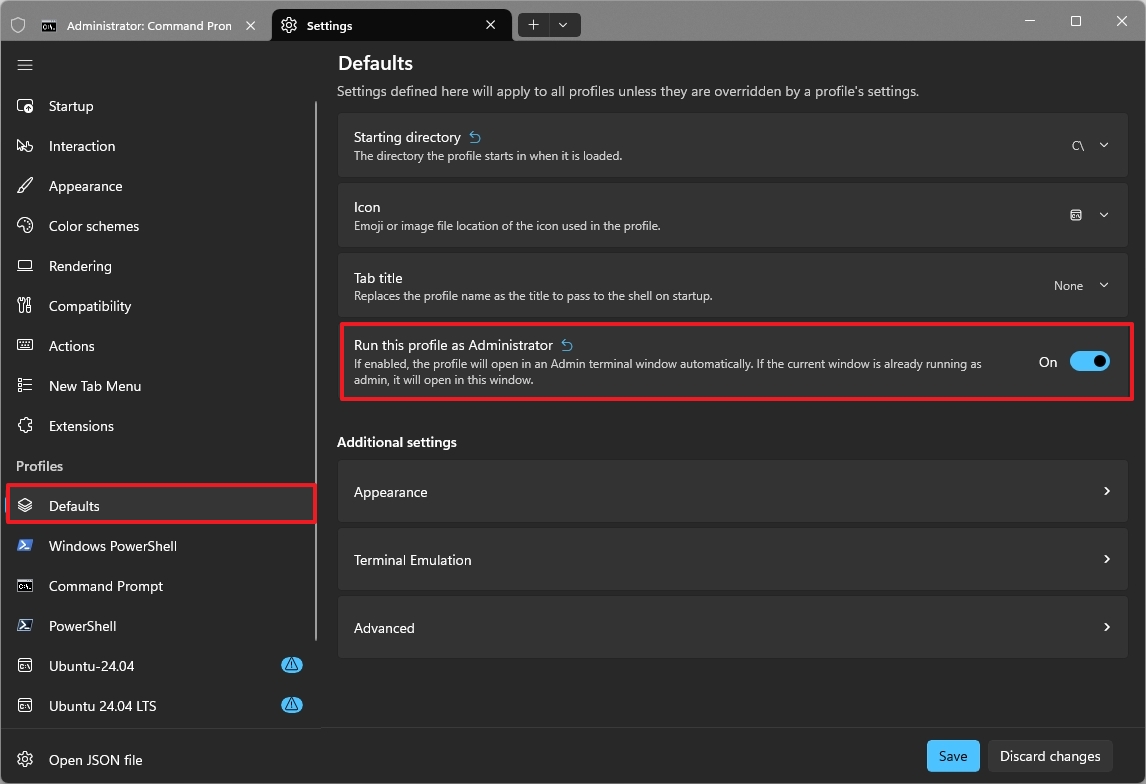
4. Always launch Windows Terminal with administrator privileges
You should always run Command Prompt or PowerShell as a standard user to follow the Principle of Least Privilege, improving security and preventing accidental execution of commands that can negatively affect the system experience.
However, if you find yourself elevating the Terminal more often than not, you can configure the application to always launch as an administrator.
To always run the Windows Terminal as an administrator, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Windows Terminal and click the top result to open the app.
- Click the main menu and choose the Settings (Ctrl+,) option.
- Quick note: Changes made under "Defaults" apply globally to every Terminal profile. To customize a single shell, select that specific profile from the list and adjust its settings individually.
- Click on Defaults.
- Turn on the "Run this profile as Administrator" toggle switch.
- Click the Save button.
After you complete the steps, every time you start the Command Prompt, PowerShell, or any other shell, the Windows Terminal will launch with administrative privileges.
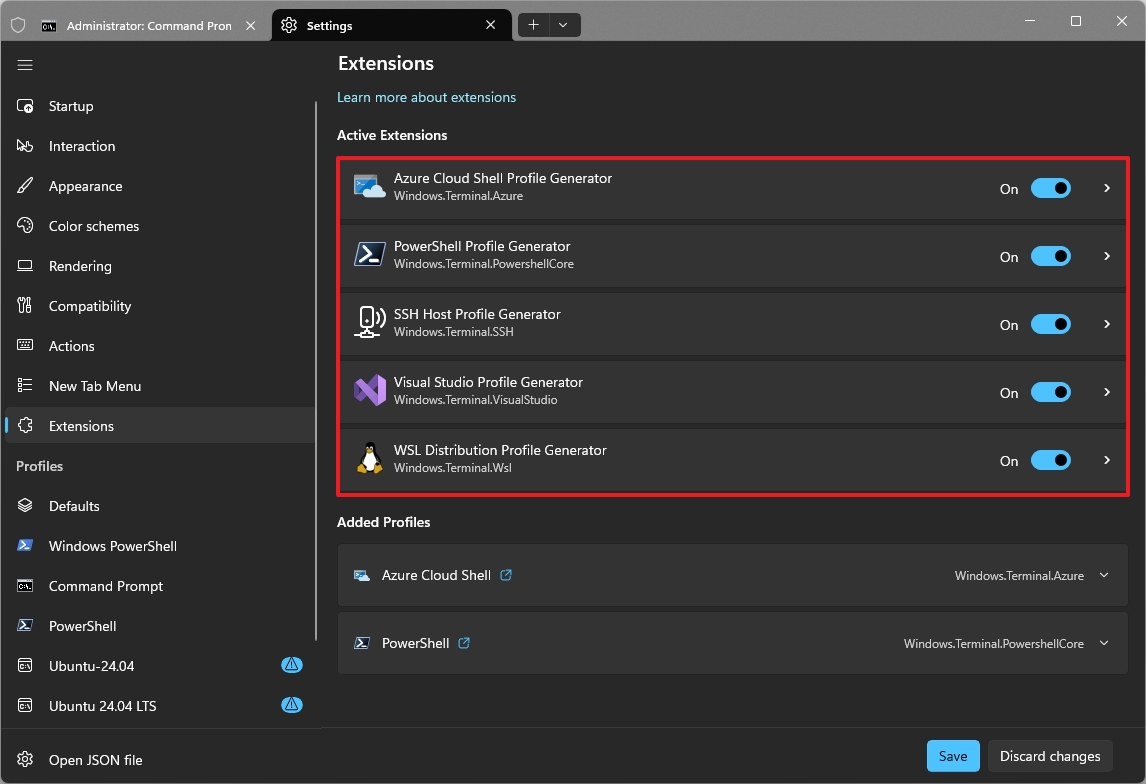
5. Turn off unnecessary Terminal extensions
Microsoft recently introduced extensions for the Windows Terminal, but they're not like "extensions" in the way a web browser like Chrome does. Instead, it uses JSON Fragment Extensions and Shell Plugins to add new features.
To turn off extensions from Windows Terminal, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Windows Terminal and click the top result to open the app.
- Click the main menu and choose the Settings (Ctrl+,) option.
- Click on Extensions.
- Turn off the toggle switch for the extensions you don't want to use.
- Click the Save button.
Once you complete the steps, the fragments of configurations that represent each extension will be stripped out of the JSON file.
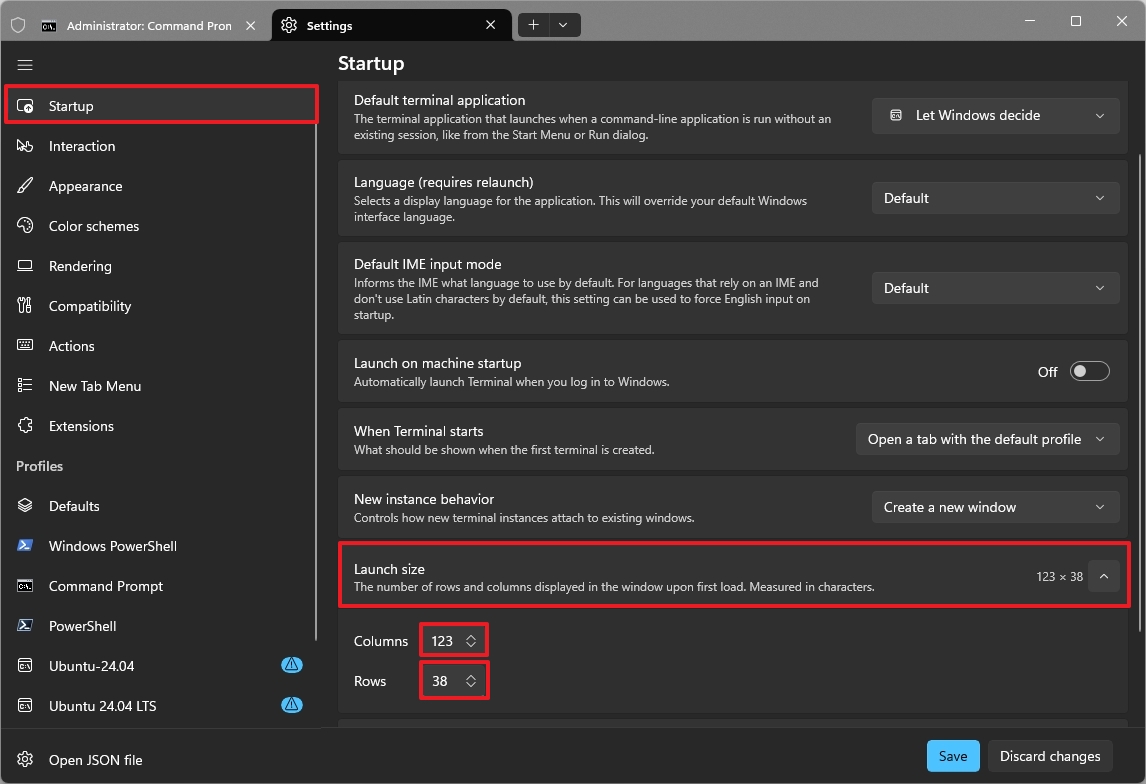
6. Set a custom default window size for all shells
By default, Windows Terminal opens at 120 columns by 30 rows, which gives the shell a noticeably rectangular layout. If you find yourself frequently resizing the window with the mouse, setting a larger default size upfront can make the experience far more comfortable.
To change the default application frame size, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Windows Terminal and click the top result to open the app.
- Click the main menu and choose the Settings (Ctrl+,) option.
- Click on Startup.
- Click the Launch size setting.
- Choose the number of columns and rows.
- Quick note: This configuration is up to your preferences. I like a more square shape, so I typically use 123 for "Columns" and 38 for "Rows."
- Click the Save button.
After you complete the steps, the Windows Terminal will launch with the specified window size.
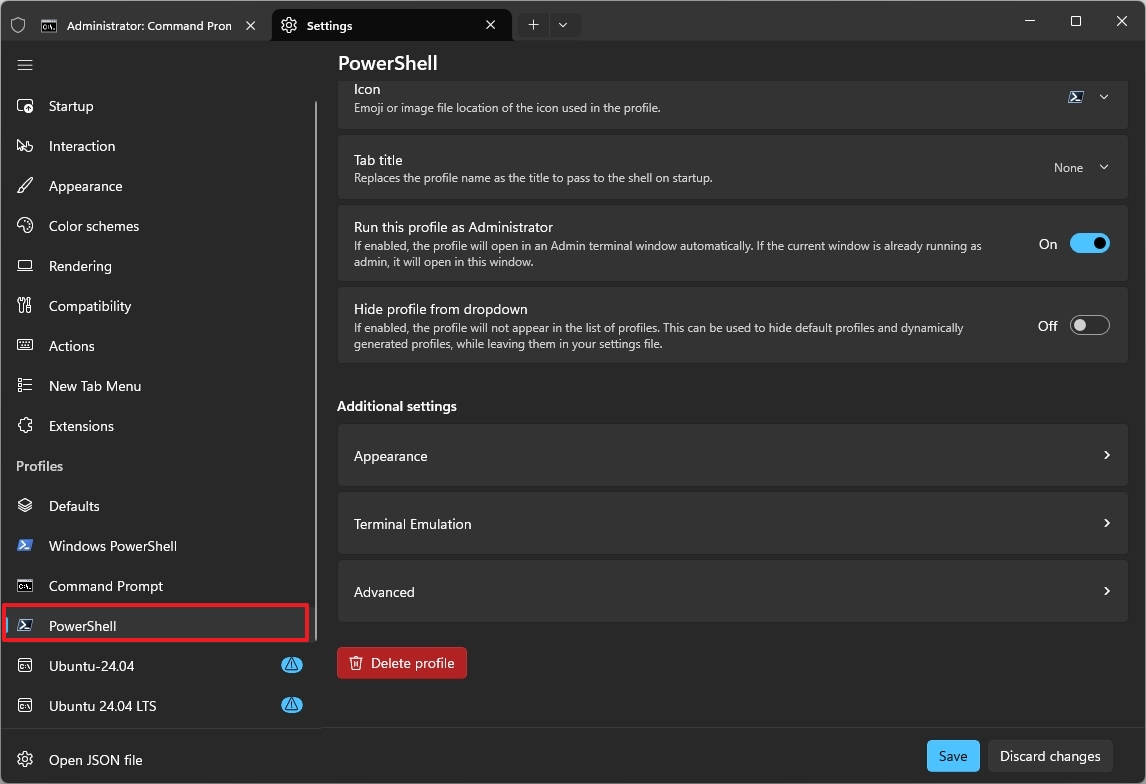
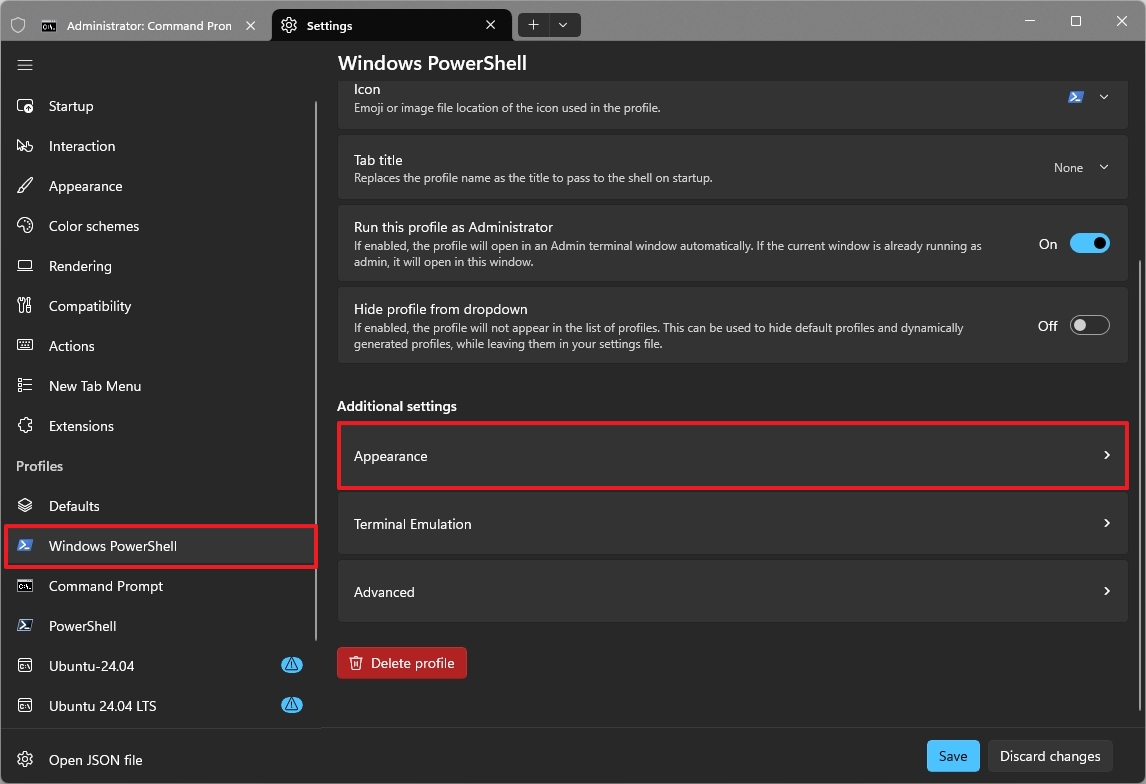
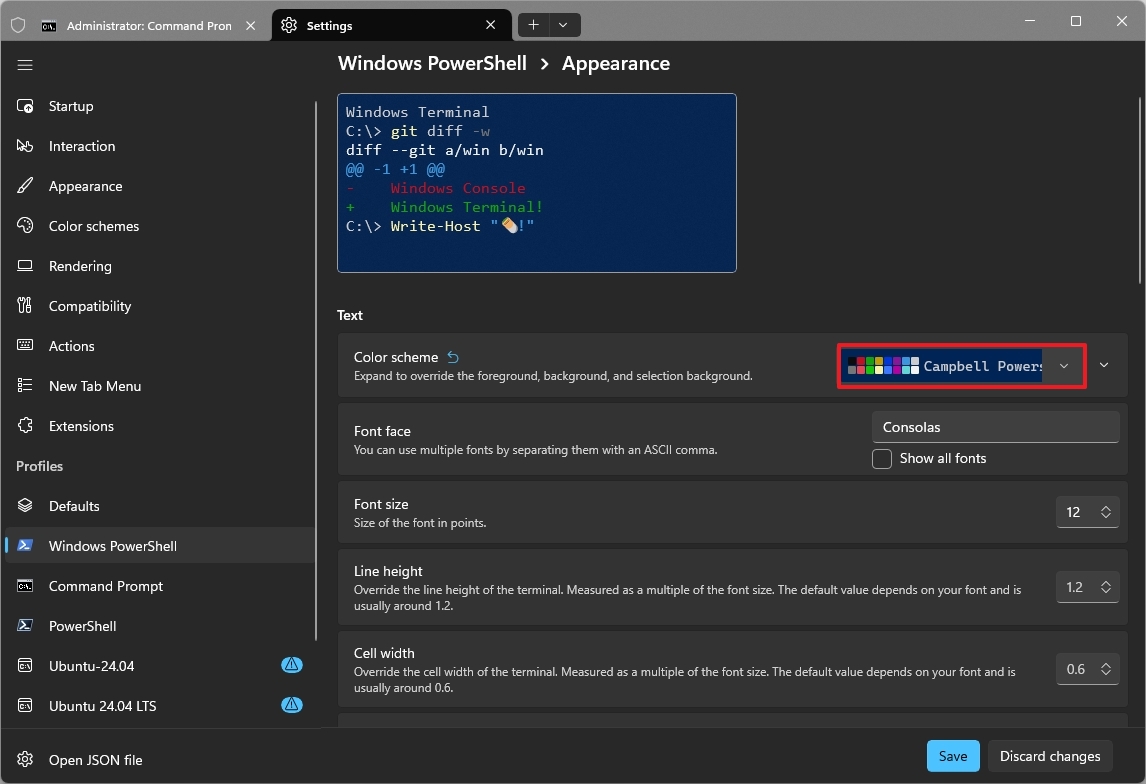
7. Restore the classic blue color scheme in PowerShell
The application sets a new dark background color scheme for all the available profiles. However, if you miss the legacy blue background in PowerShell, you can restore it from the profile's appearance settings.
To restore the familiar dark blue color scheme for PowerShell, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Windows Terminal and click the top result to open the app.
- Click the main menu and choose the Settings (Ctrl+,) option.
- Click on Windows PowerShell.
- Click the Appearance setting under the "Additional settings" section.
- Choose the Campbell PowerShell option in the "Color scheme" setting.
- Click the Save button.
Once you complete the steps, you'll be able to interact with the command-line interface using the familiar dark blue color scheme, as in the legacy version.
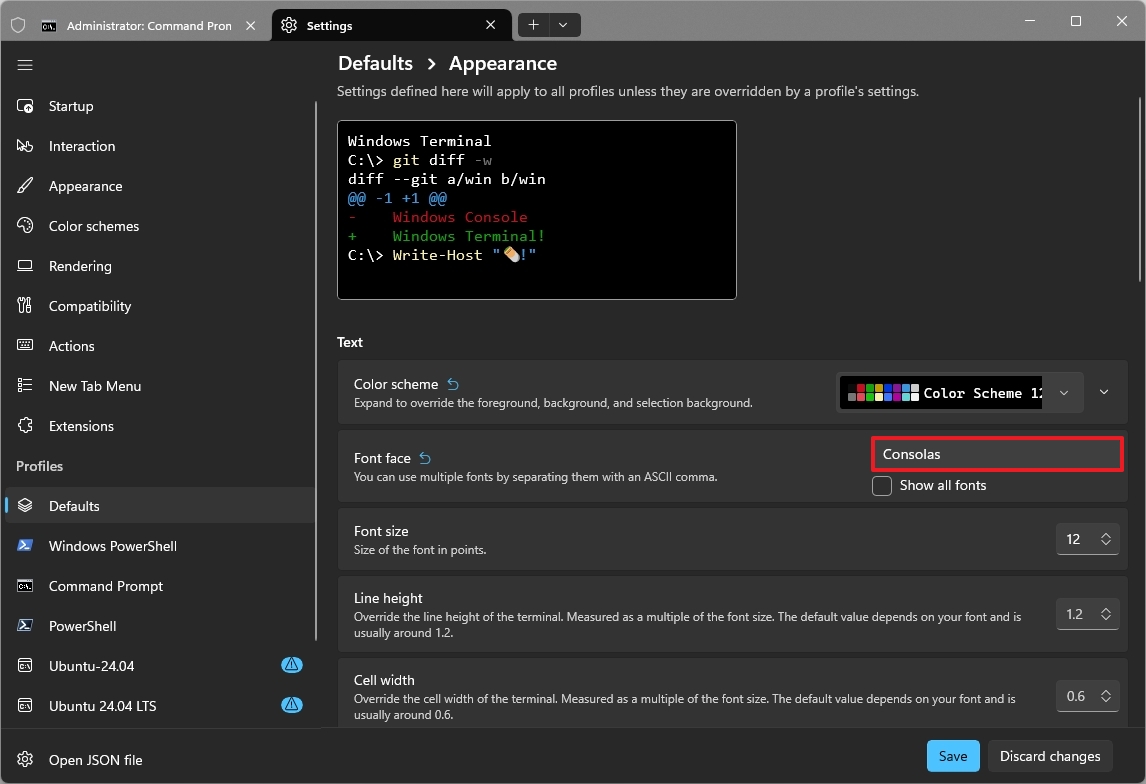
8. Change the font family for better readability
Although the legacy version of Command Prompt uses the "Consolas" font, Windows Terminal defaults to "Cascadia Mono". However, you can always switch to the "Consolas" font.
To restore the Command Prompt's font family when using the Windows Terminal, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Windows Terminal and click the top result to open the app.
- Click the main menu and choose the Settings (Ctrl+,) option.
- Click on Defaults.
- Click the Appearance setting under the "Additional settings" section.
- Choose the Consolas font family in the "Font face" setting.
- Click the Save button.
After you complete the steps, the Terminal will use a more traditional font experience when running commands in PowerShell, Command Prompt, or another shell you may have configured on your computer.
9. Back up and restore your Windows Terminal settings
Lastly, I always keep a backup of my configuration so that I can easily import it to other devices for a more consistent experience.
Backup Terminal settings
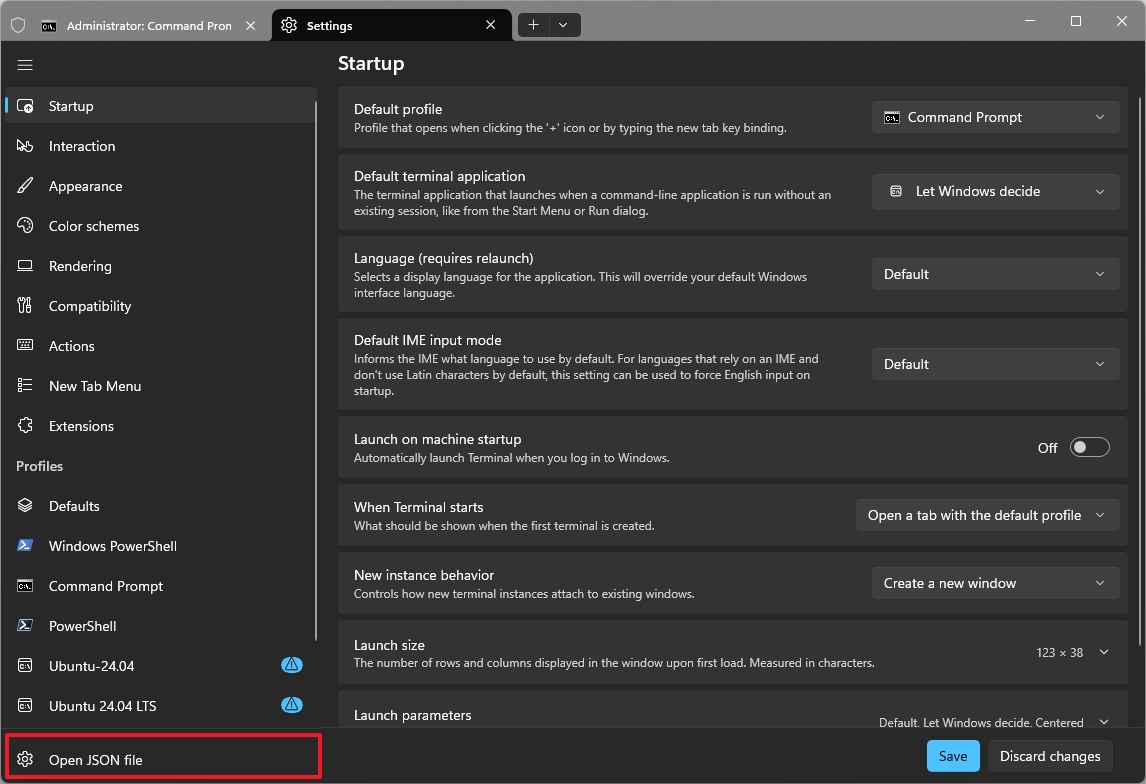
To export your Windows Terminal settings, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Windows Terminal and click the top result to open the app.
- Click the main menu and choose the Settings (Ctrl+,) option.
- Click on Open JSON file.
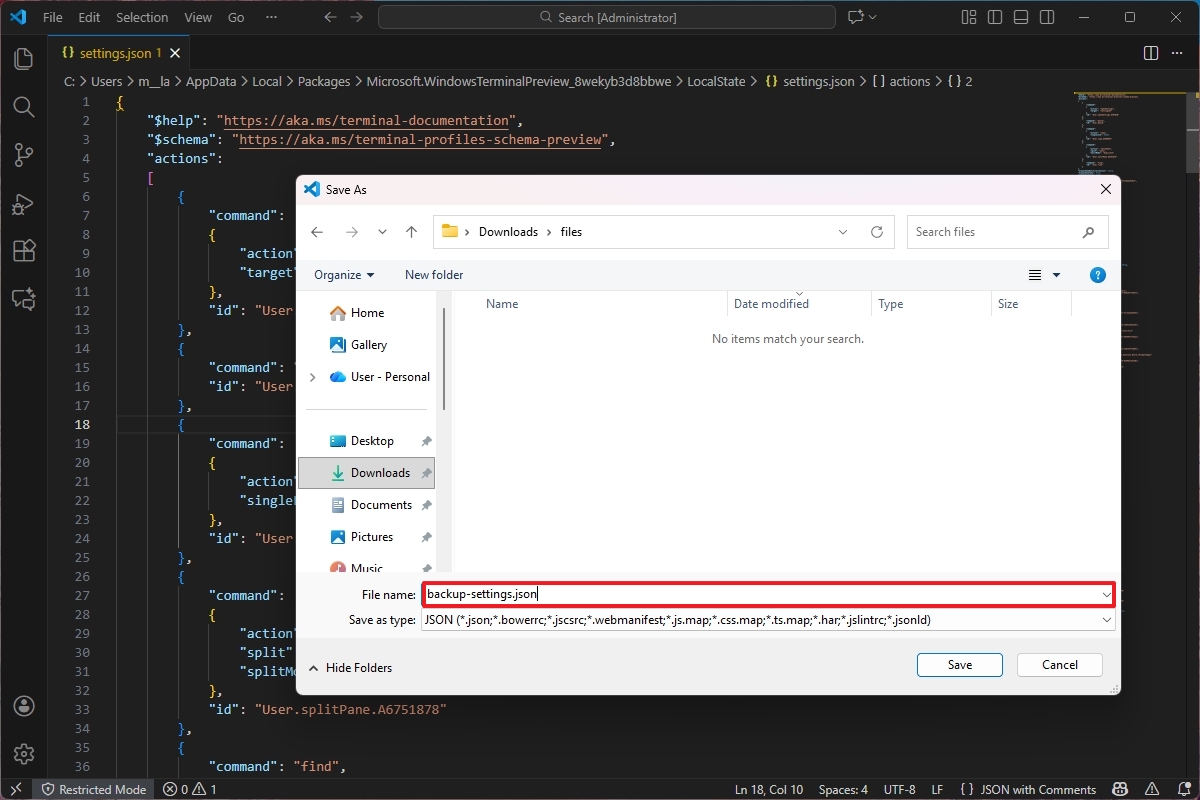
- Click the File menu and choose the Save As option.
- Select the location to save the file.
- Change the name to backup-settings.json.
- Click the Save button.
Once you complete the steps, all the customization settings will be exported to a JSON file, which you can use to restore your custom configuration on the same device after making changes or on another computer.
Restore Terminal settings
To import your Terminal settings to the same or a different computer, use these steps:
- Open the backup file location.
- Right-click the backup-settings.json and choose the "Edit in Notepad" option.
- Select everything using the "Ctrl + A" and "Ctrl + C" keyboard shortcuts.
- Open Start.
- Search for Windows Terminal and click the top result to open the app.
- Click the main menu and choose the Settings (Ctrl+,) option.
- Click on Open JSON file.
- Select everything using the "Ctrl + A" keyboard shortcut and click the Delete button.
- Use the "Ctrl + V" keyboard shortcut to paste the configuration from backup.
- Use the "Ctrl + S" shortcut to save the configuration.
After you complete the steps, the custom settings will be applied immediately, discarding the previous configuration.
Do you have a specific customization that you always apply to the Windows Terminal? Let me know in the comments.
FAQs about customizing Windows Terminal
These are common questions regarding changing the Windows Terminal settings on Windows 11.
Can I set a different default shell other than Command Prompt in Windows Terminal?
Yes. Windows Terminal allows you to set any installed shell (PowerShell, WSL distributions, or third-party terminals) as the default startup profile. You can change this under Settings > Startup > Default profile.
How do I make Windows Terminal always open in a specific folder?
You can configure a global starting directory for all shells. Open Settings > Defaults > Starting directory, select your preferred folder, and save the changes.
Is it safe to delete unused Terminal profiles?
Yes, it is safe as long as you do not delete the legacy "Windows PowerShell" profile if you still use it. Removing unused profiles declutters the Terminal interface and makes switching between shells faster.
Can I always run Windows Terminal as administrator by default?
Yes. Under Settings > Defaults, enable the "Run this profile as Administrator" toggle. Use this cautiously, as running as admin all the time can expose your system to accidental changes.
How can I change the default window size for the Terminal?
Go to Settings > Startup > Launch size and specify your preferred number of columns and rows. This avoids resizing the window each time you open the Terminal.
Can I restore the classic PowerShell blue color scheme?
Yes. Open Settings > Windows PowerShell > Appearance > Color scheme and select "Campbell PowerShell." This brings back the familiar blue background from legacy PowerShell.
How do I change the font for better readability?
Under Settings > Defaults > Appearance > Font face, select your preferred font, such as "Consolas," for a more traditional Command Prompt experience.
How can I back up and restore my Terminal settings?
You can export settings via Settings > Open JSON file > Save As, and import them on the same or another computer by pasting the JSON content back into the Terminal’s JSON file. This ensures consistency across devices.
More resources
Explore more in-depth how-to guides, troubleshooting advice, and essential tips to get the most out of Windows 11 and 10. Start browsing here:
- Windows 11 on Windows Central — All you need to know
- Windows 10 on Windows Central — All you need to know

Follow Windows Central on Google News to keep our latest news, insights, and features at the top of your feeds!

Mauro Huculak has been a Windows How-To Expert contributor for WindowsCentral.com for nearly a decade and has over 22 years of combined experience in IT and technical writing. He holds various professional certifications from Microsoft, Cisco, VMware, and CompTIA and has been recognized as a Microsoft MVP for many years.
You must confirm your public display name before commenting
Please logout and then login again, you will then be prompted to enter your display name.