10 essential maintenance tips to keep your Windows 11 PC running longer — reduce slowdowns and reclaim performance
These tips can help your computer last years longer without upgrades.
All the latest news, reviews, and guides for Windows and Xbox diehards.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
On Windows 11, performing basic maintenance can help extend the lifespan of your computer. In this guide, I outline (several) practical ways to keep your device running reliably for years to come.
Computer hardware is no longer getting cheaper. System memory prices continue to increase with no sign of slowing, storage costs are climbing, and even entry-level computers now cost significantly more than they did just a few years ago. Replacing a perfectly usable device has become an expensive decision rather than a routine upgrade.
The good news is that Windows 11 includes tools that (when used correctly) can help you extend the usable life of your current system, and in this set of instructions, I'll show you close to a dozen ways to complete this task.
Article continues belowIn this how-to guide, I'll dive into simple tips to help you keep your device for years to come.
Top 10 maintenance tips everyone should know on Windows 11
On Windows 11, you can take many steps to help extend your device's usable life, and here are 10 of them.
1. Software maintenance is a way to avoid costly upgrades
When memory and storage prices are high, inefficiencies become expensive. A bloated system consumes more memory, uses more storage space, and creates the illusion that hardware is failing when it is not.
Keeping the operating system clean and stable ensures you are using every gigabyte of memory and storage you already paid for.
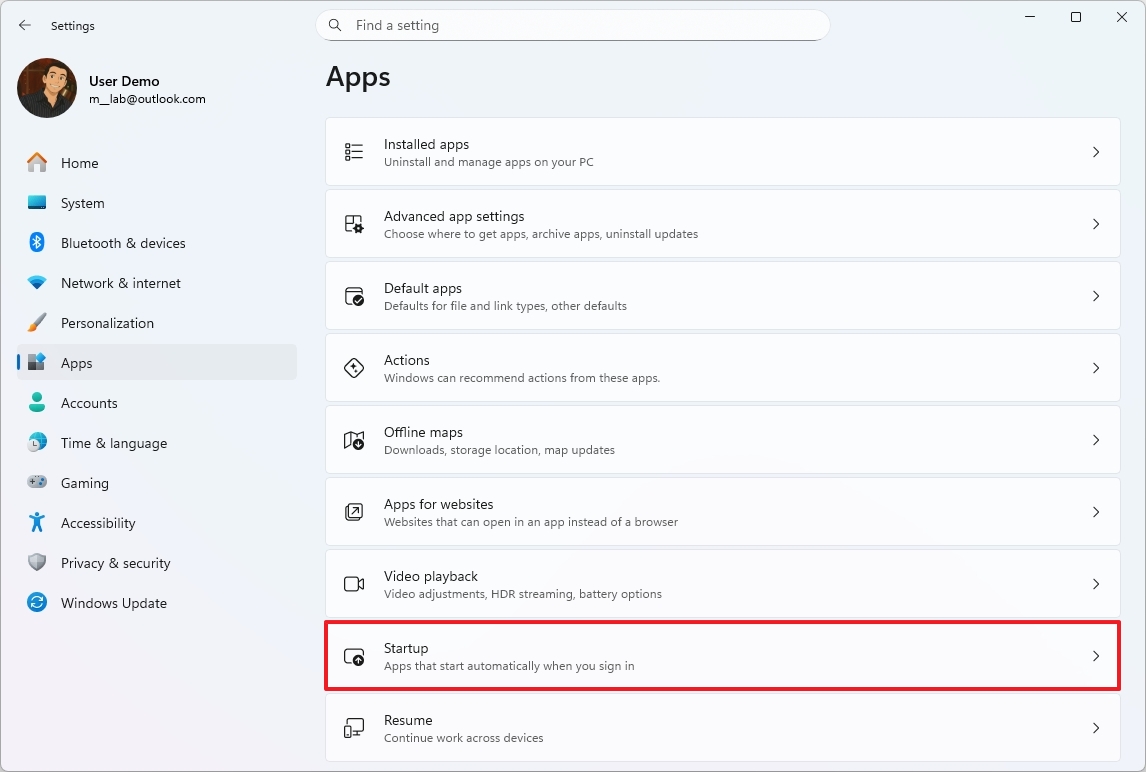
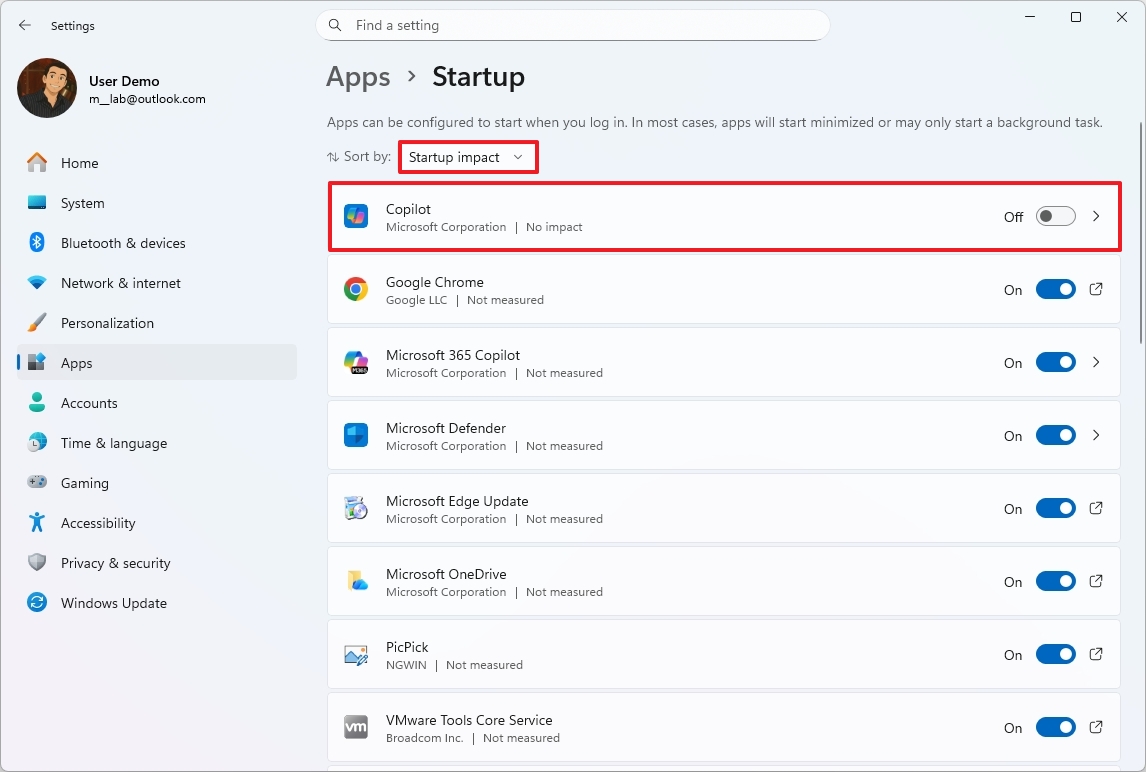
Control apps at startup
To prevent specific apps from running at startup, use these steps:
- Open Settings.
- Click on Apps.
- Click the Startup page on the right side.
- Select the Startup impact option in the "Sort by" setting.
- Turn off the applications impacting the most performance.
After you complete these steps, your computer will start faster and use fewer system resources. This frees up processing power and memory for other tasks, resulting in a noticeably snappier experience. Of course, the performance gains depend on how many resources you are able to reclaim using this approach.
You can also uninstall unnecessary apps, and I will show you how to do this in the steps below.
2. Keep Windows 11 updated to protect your hardware investment
Security updates do more than protect your data. They also patch vulnerabilities that can damage system files, break drivers, or even force an unnecessary reinstallation of the operating system.
I realize that this is a double-edged sword. The update quality, particularly with recent Windows 11 releases, has occasionally introduced stability issues. However, keeping your device up to date remains the recommended approach. Beyond security and performance improvements, an unpatched system is more likely to be compromised, which can trigger failures that push users to replace hardware unnecessarily.
Preventing system failure is far cheaper than replacing a computer or upgrading critical components.
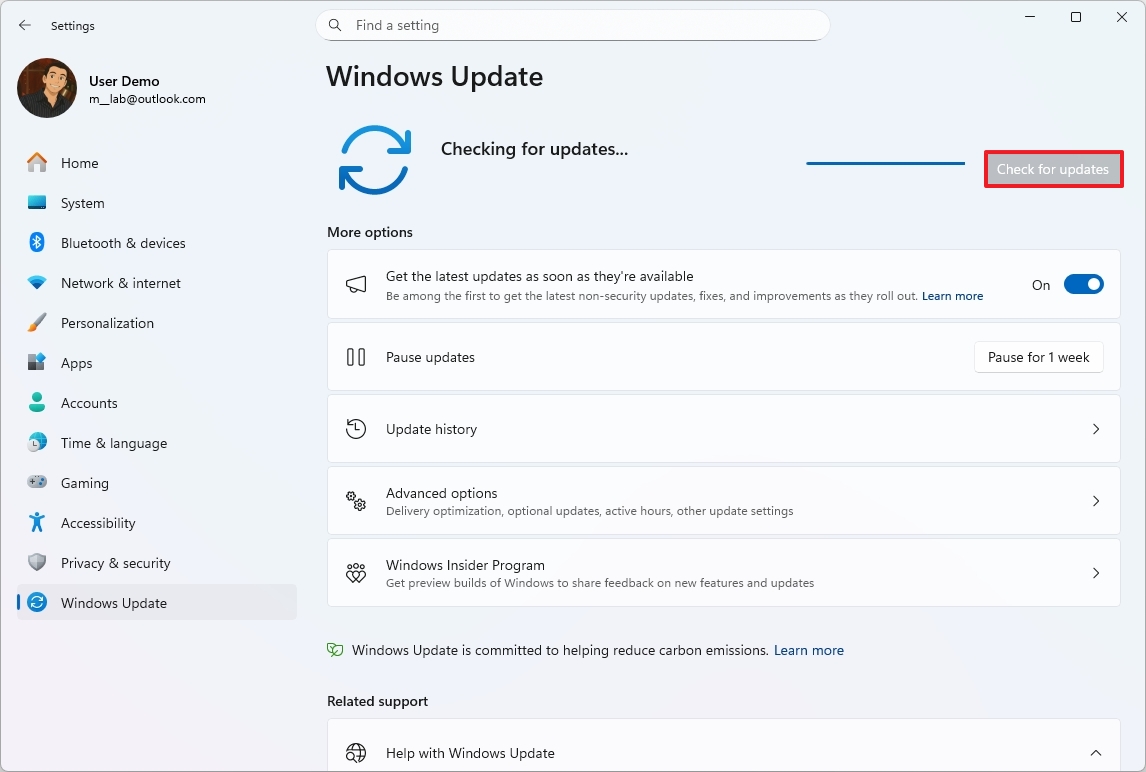
Install system updates manually
Although the operating system installs updates manually, you can always check for updates manually with these steps:
- Open Settings.
- Click on Windows Updates.
- Click the "Check for updates" button.
Once you complete the steps, the computer will download and install the latest update available.
Alternatively, you can also download and install the packages manually from the Microsoft Update Catalog website to update Windows 11.
3. Reduce memory usage by controlling startup apps
High memory usage is one of the main reasons you may feel your computer is getting old. In many cases, systems struggle because too many apps launch automatically and remain in memory.
Windows 11's startup settings let you disable nonessential apps at startup without uninstalling them. You can also turn off nonessential system and app features. In addition, excessive memory usage can indicate a malware problem.
Remember that lowering RAM usage can delay the need for expensive memory upgrades.
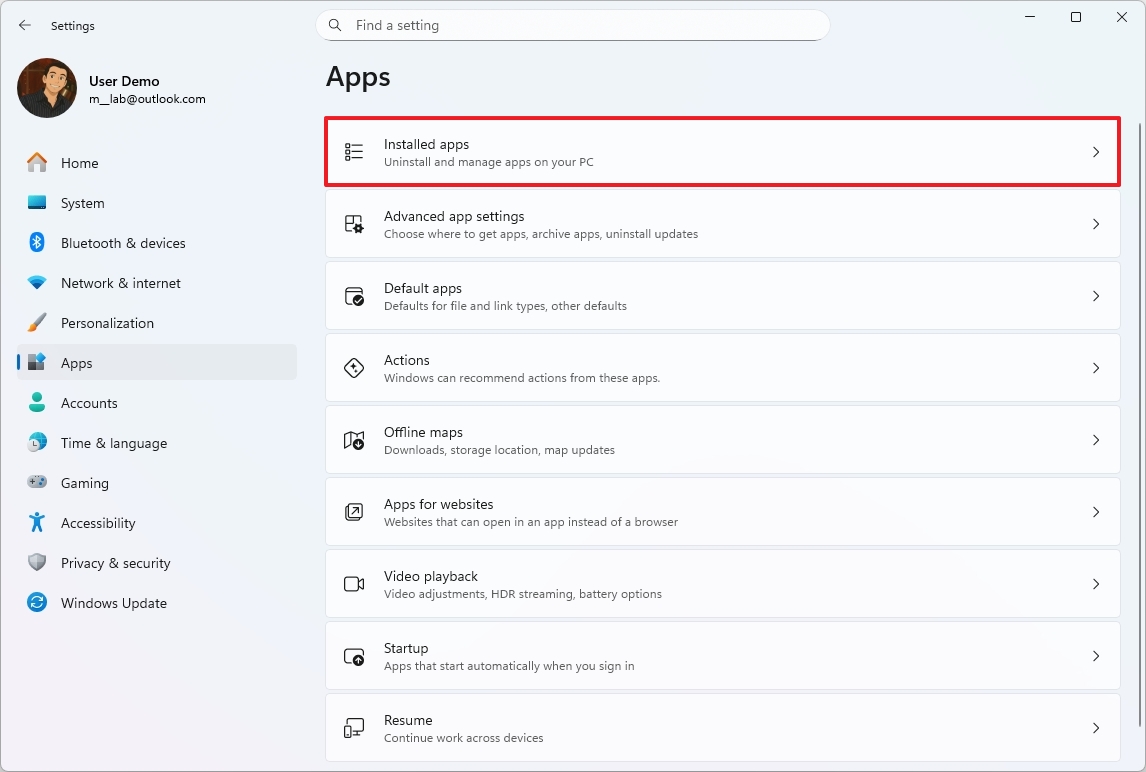
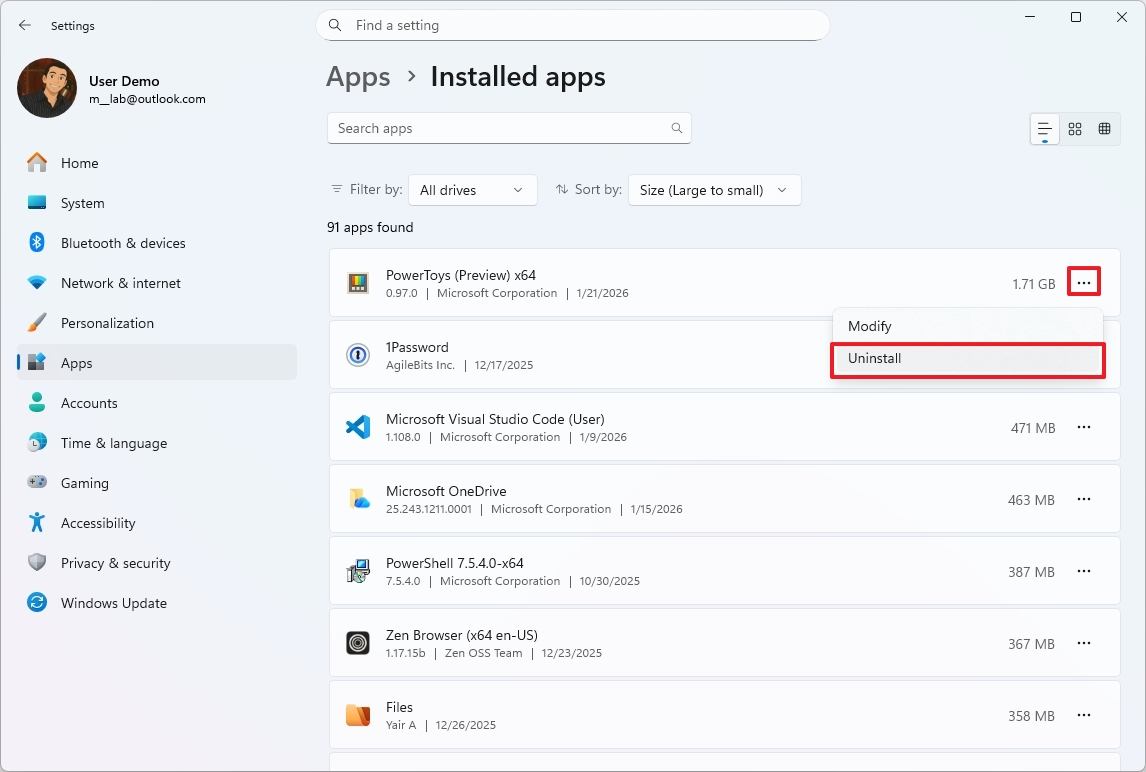
Uninstall unused apps
In addition to disabling apps at startup (as shown above), it's also recommended to uninstall programs you no longer use (including games). This helps free up storage space and system resources. Here's how:
- Open Settings.
- Click on Apps.
- Click the Installed app page on the right side.
- Open the app's menu from the right side and click the Uninstall option.
- Click the Uninstall option one more time.
- Continue with the on-screen directions (if applicable).
Once you complete the steps, you may need to repeat the instructions to uninstall other apps (and games) you may not use.
Full antivirus scan
To confirm that malware isn't taking your system's RAM hostage, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Windows Security and click the top result to open the app.
- Click on Virus & threat protection from the left pane.
- Click on Scan options.
- Select the Full scan option.
- Click the Scan now button.
After you complete the steps, the antivirus will scan, detect, and remove any malware affecting your device.
If the memory usage is still higher than usual after the scan and you suspect the problem is due to a virus, you can also perform a malware offline scan.
In addition, you can perform other steps to reduce the memory consumption. For example, you can turn off unnecessary system services and features, and use tools like the Microsoft PC Manager, which includes features specifically designed to reduce system memory usage.
4. Reclaim storage that you cannot easily replace
Storage upgrades are no longer as cheap as they once were, especially for fast NVMe drives. Every unused app, cache, and background service consumes space that the operating system needs to function efficiently.
Regularly uninstalling unused programs and clearing junk files can free up space to keep usage under control. However, avoid aggressive cleanup tools, as they can remove files or Registry entries that are still needed, causing instability that may lead to reinstalls or hardware swaps.
Also, running out of storage leads to performance drops, failed updates, and unnecessary drive replacements.
Free up storage space
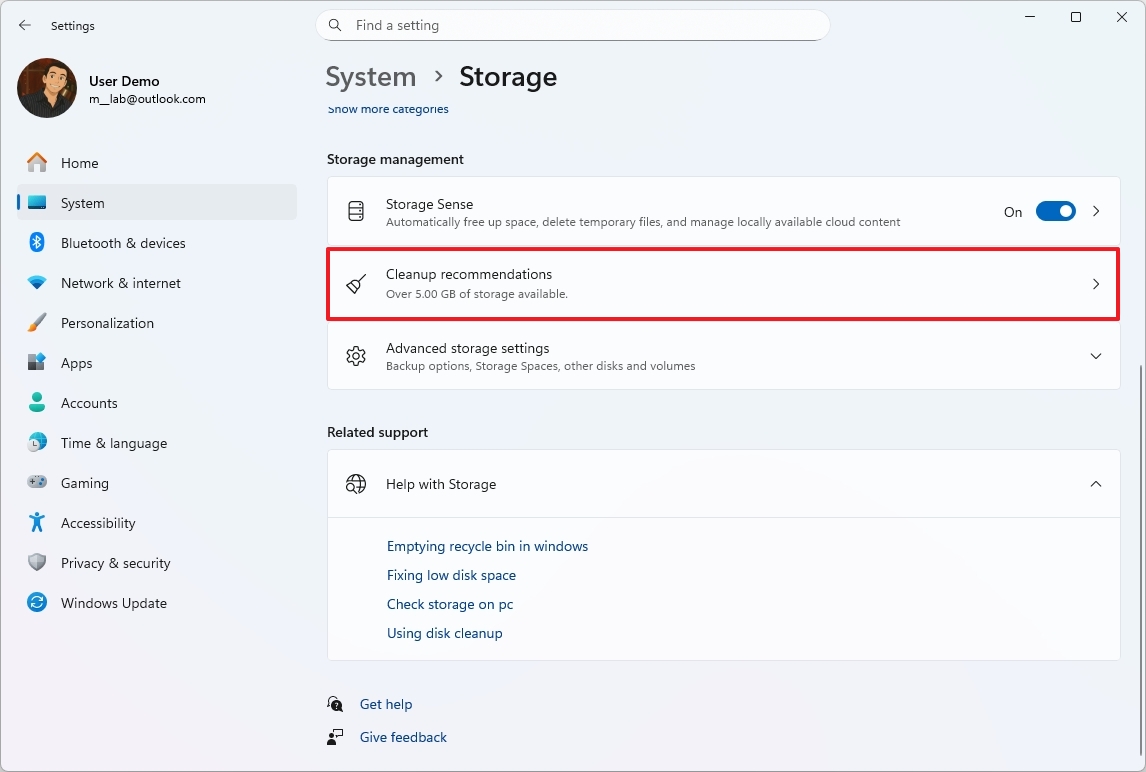
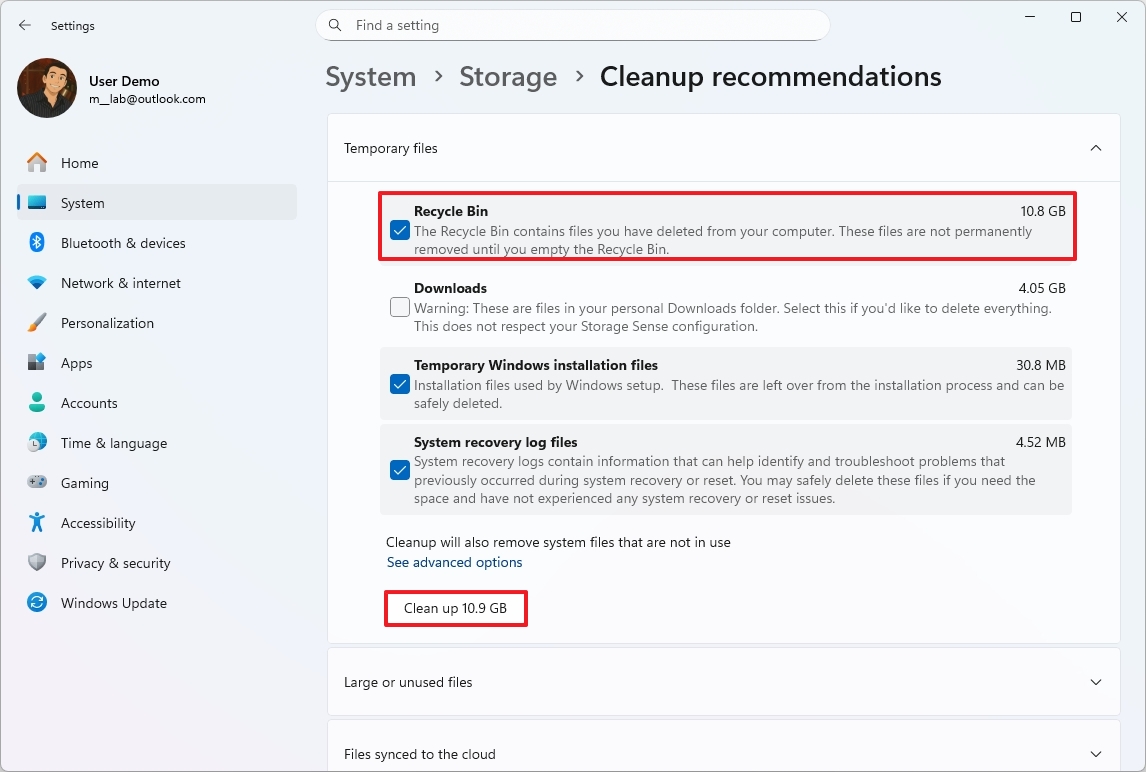
On Windows 11, you can reclaim storage in many ways, but the "Cleanup recommendations" feature is perhaps the first you should use because it automatically tells you which files you can remove from your laptop or desktop.
To free up space with Cleanup recommendations on Windows 11, use these steps:
- Open Settings.
- Click on System.
- Click the Storage page on the right side.
- Under the "Storage management" section, select the "Cleanup recommendations" setting.
- Click on Temporary files.
- Select the files to delete to free up space.
- Click the Clean up button.
- Click on "Large or unused files."
- Select the large and unused files to delete.
- Click the Clean up button.
- Click on "Files synced to the cloud."
- Select the synced files that you can delete locally.
- Quick note: If you delete synced files, they will still be available on your OneDrive account.
- Click on Unused apps.
- Check the recommended apps that you can delete to free up space on Windows 11.
- Click the Clean up button.
Once you complete the steps, the content will be deleted from the system, freeing up space for more important files.
5. Preserve SSD health to avoid early replacement
Solid-State Drives (SSDs) wear out faster when nearly full or constantly writing unnecessary data due to how NAND flash memory operates. Keeping free space available and avoiding excessive background activity helps reduce write amplification.
Maintaining the health of an SSD is mostly about reducing unnecessary writes, keeping the firmware up to date, and avoiding conditions that accelerate wear. Here are the most effective practices:
Keep free space available
SSDs need free space for wear leveling and garbage collection. Typically, I recommend never filling the storage drive past 70 percent to prevent performance issues and improve longevity.
Avoid unnecessary write-heavy tasks
Frequent small-block random writes, excessive logging, and constant benchmarking increase write amplification. Although large sequential rewrites place more stress on the flash memory, they are generally more efficient for the SSD controller than scattered, small updates, which trigger additional internal data movement.
Do not defragment a Solid-State Drive
Defragmentation doesn't provide any benefits on SSDs and only adds unnecessary writes that can shorten the drive's lifespan. Instead, Windows 11 uses TRIM, a feature that informs the SSD which data blocks are no longer in use so they can be wiped internally.
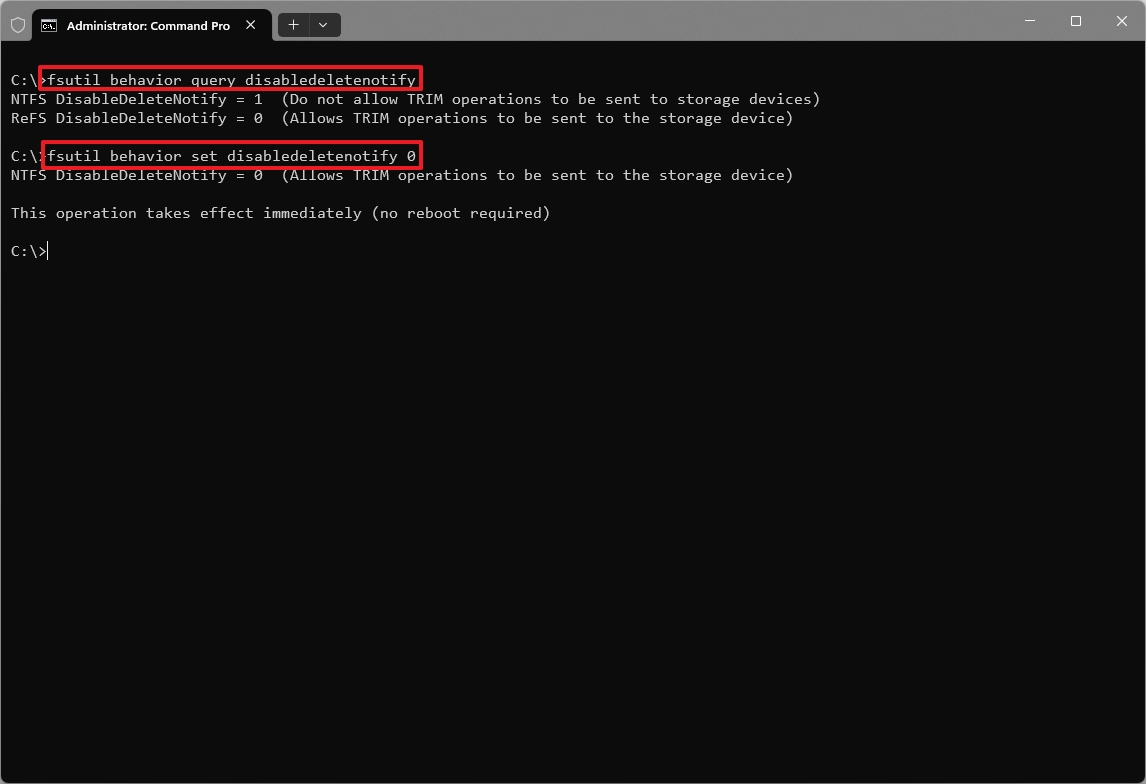
While the operating system enables this by default, you may want to verify that your system is optimized correctly. To check and enable TRIM on Windows 11, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Command Prompt, right-click the top result, and choose the Run as administrator option.
- Type the following command to confirm whether TRIM is enabled or disabled and press Enter: fsutil behavior query disabledeletenotify
- Confirm the output, the "NTFS DisableDeleteNotify = 0" result means enabled, and the "NTFS DisableDeleteNotify = 1" means disabled.
- Type the following command to enable TRIM and press Enter: fsutil behavior set disabledeletenotify 0
- Type the following command to confirm the state of the feature and press Enter: fsutil behavior query disabledeletenotify
Once you complete the steps, the TRIM feature will be enabled on Windows 11.
Keep firmware and system updates current
SSD firmware updates often improve stability, performance, and wear management. As a result, ensuring the storage device is up to date can help extend its lifespan.
However, since the update processes vary by manufacturer, it's recommended to check the manufacturer's support website to download the tool and find the specific steps to complete the update.
Finally, I would only suggest updating the storage firmware if the hardware vendor pushes a critical update that requires immediate action. Also, always perform a backup of the storage before updating the firmware.
Manage temperatures
Using an SSD at not suitable temperatures can accelerate flash memory degradation. Ensure proper airflow, avoid sustained heavy writes without cooling, and keep laptops well ventilated.
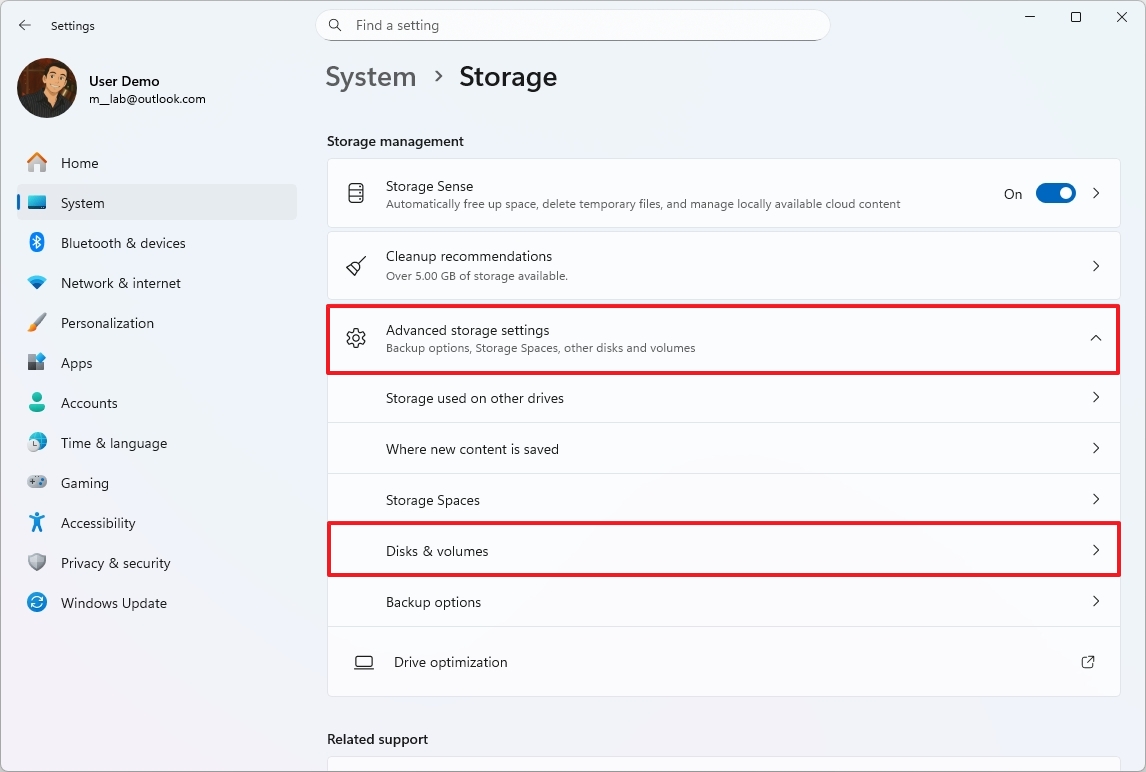
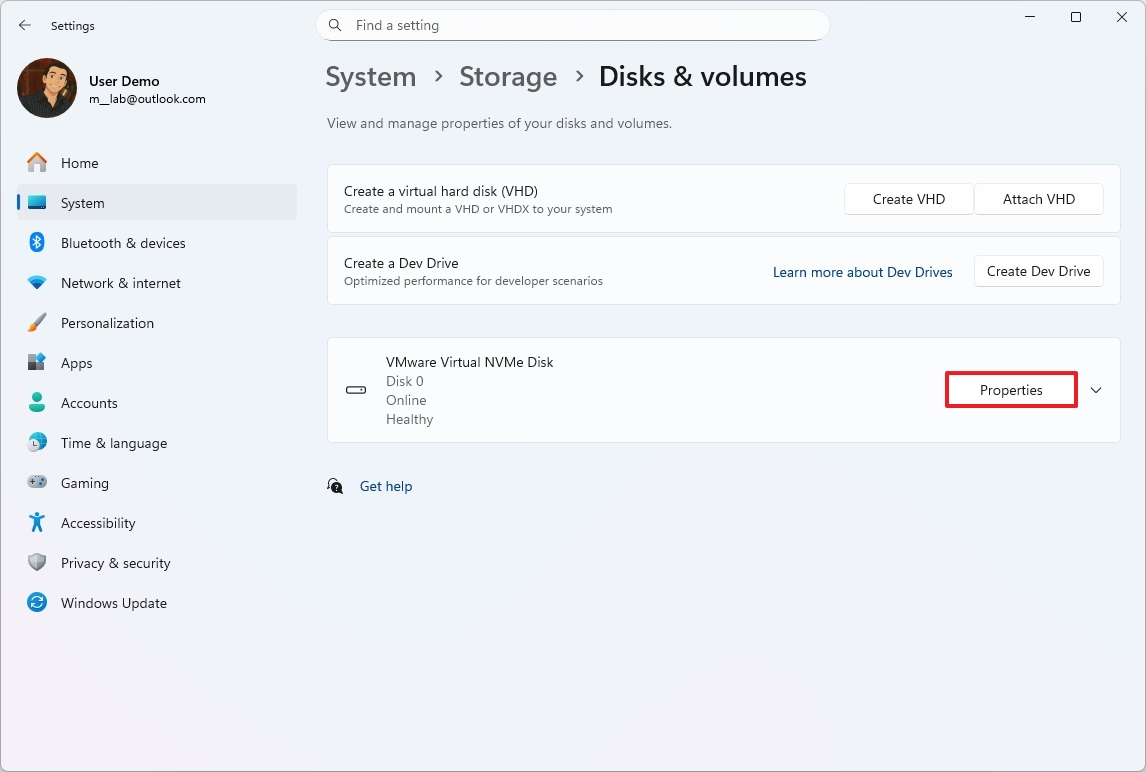
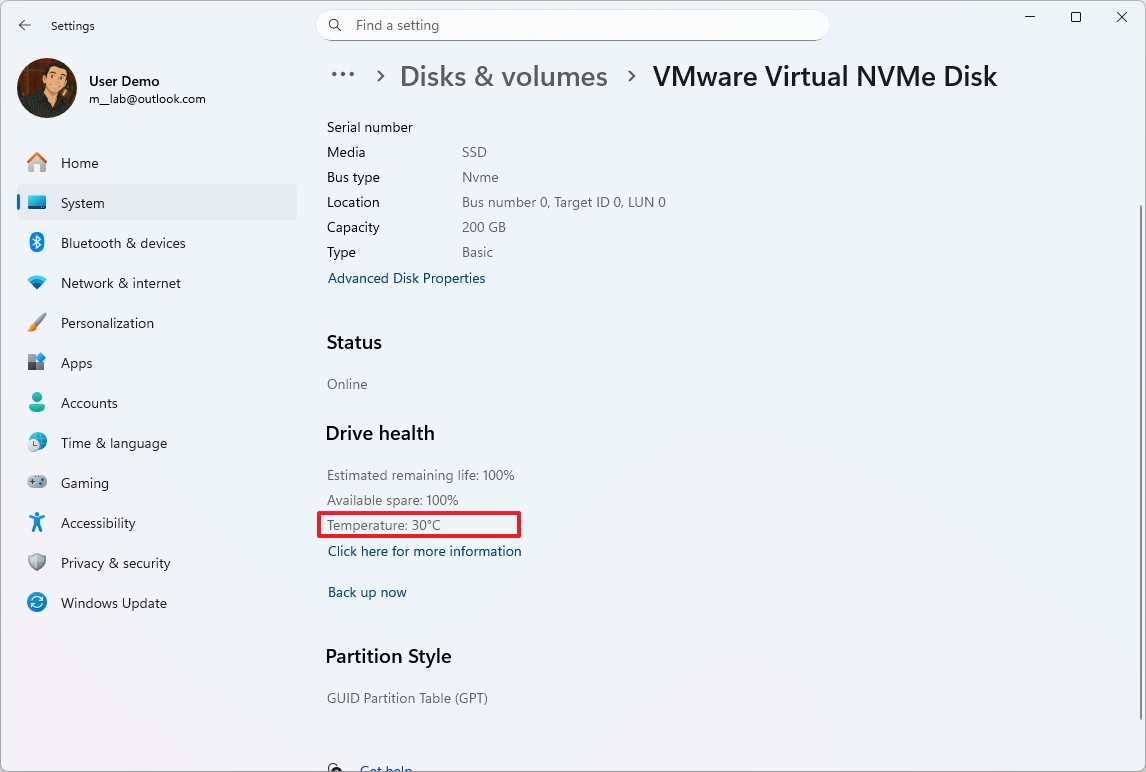
To check the SSD temperature on Windows 11, use these steps:
- Open Settings.
- Click on System.
- Click the Storage page on the right side.
- Select the "Advanced storage settings" option under the "Storage management" section.
- Click on Disks & volumes.
- Click the Properties button for the drive.
- Confirm the current temperature under the "Drive health" section.
After you complete the steps, you'll have an understanding of the drive temperature.
Under load, if the temperature is under 70 degrees Celsius, then the drive is operating at an acceptable temperature. Over 70 degrees Celsius is typically considered the upper limit for consumer-grade drives.
Monitor drive health periodically
Use the manufacturer's utility or S.M.A.R.T. (Self-Monitoring, Analysis, and Reporting Technology) monitoring tools to check remaining lifespan, total writes, and error counts. This helps detect early signs of failure.
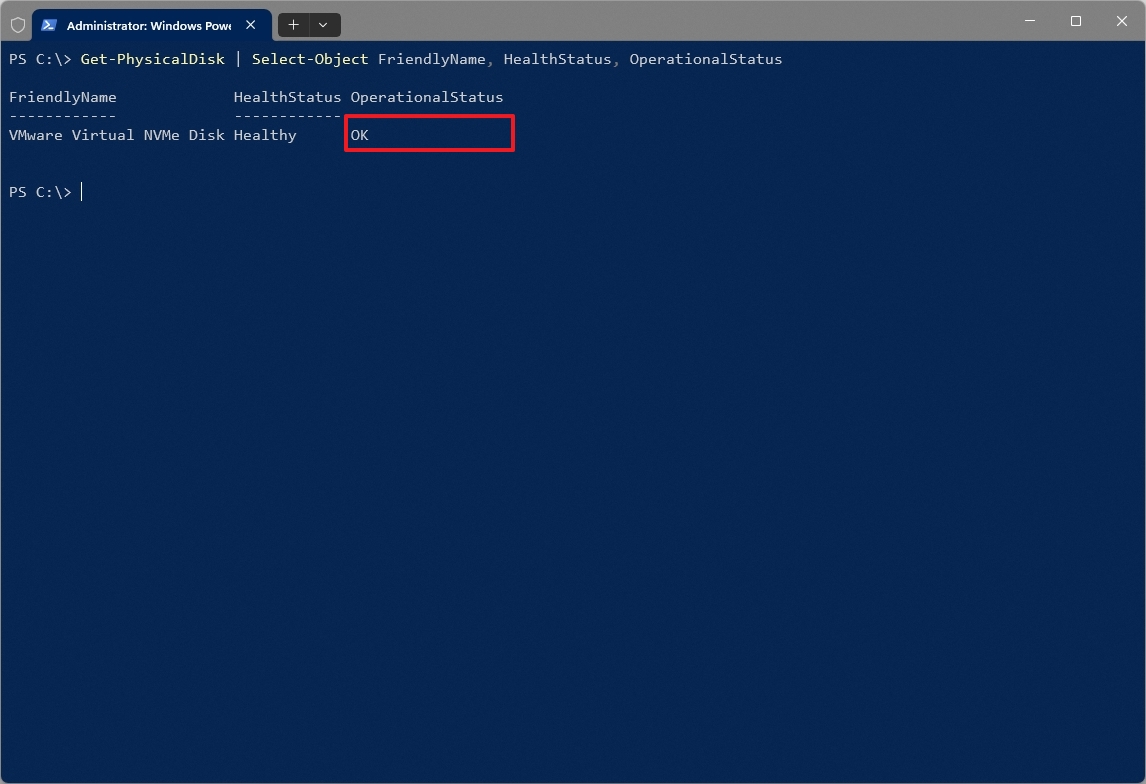
To check the drive SMART state with commands on Windows 11, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Command Prompt, right-click the top result, and choose the Run as administrator option.
- Type the following command to check the SMART feature on your drive and press Enter: Get-PhysicalDisk | Select-Object FriendlyName, HealthStatus, OperationalStatus
Once you complete the steps, the "HealthStatus" should read "Healthy," and notifications such as "Warning," "Bad," or "Caution" indicate an imminent hardware failure. The "OK" message indicates that the drive is working properly.
Repair errors and bad sectors
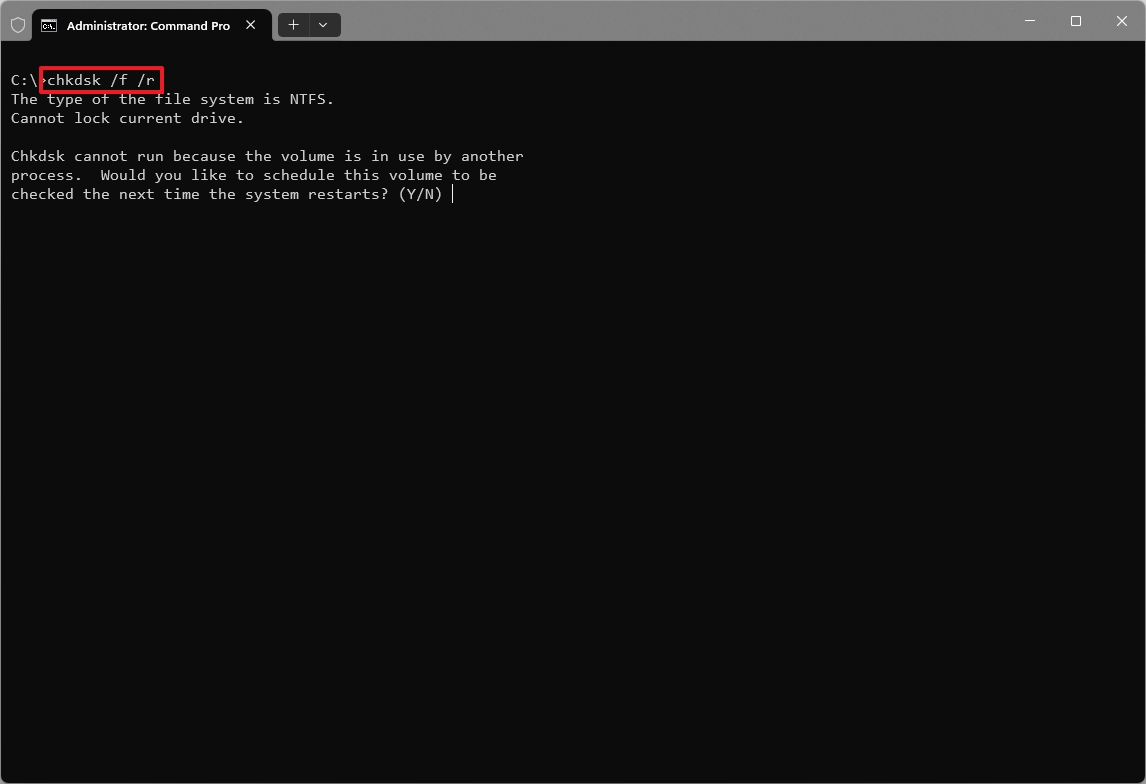
In addition to monitoring the drive's health, you can use built-in tools, such as the Check Disk utility, to detect and fix various file system errors and bad sectors:
- Open Start.
- Search for Command Prompt, right-click the top result, and choose the Run as administrator option.
- Type the following command to run the Check Disk tool on your computer and press Enter: chkdsk /f /r
- Type "Y" to schedule a scan during the next reboot.
- Restart the computer.
After you complete the steps, this tool will scan your device's SSD. It looks for "bad sectors" (physical damage to the disk) and logical errors in the file system (the index that tells the operating system where your data is).
If your current setup is experiencing logical problems, you can also use the DISM utility alongside the SFC tool troubleshoot and resolve operating system issues.
6. Use power management properly
Maintaining a laptop battery's health involves managing charge cycles, heat, and power usage. These best practices help slow long-term degradation and extend usable lifespan.
Avoid fully charging battery to 100 percent all the time
Lithium-based batteries age faster when held at full charge. If your laptop supports it, enable a charging limit, typically 80 percent, especially if the device stays plugged in most of the time.
Avoid deep discharges
Regularly draining the battery to 0 percent can increase stress on the cells. You should recharge when the battery reaches around 20 to 30 percent instead of letting it fully discharge.
Monitor battery health
Periodically check battery health reports or manufacturer utilities to track capacity loss and charging behavior. This helps you adjust usage before degradation becomes too noticeable.
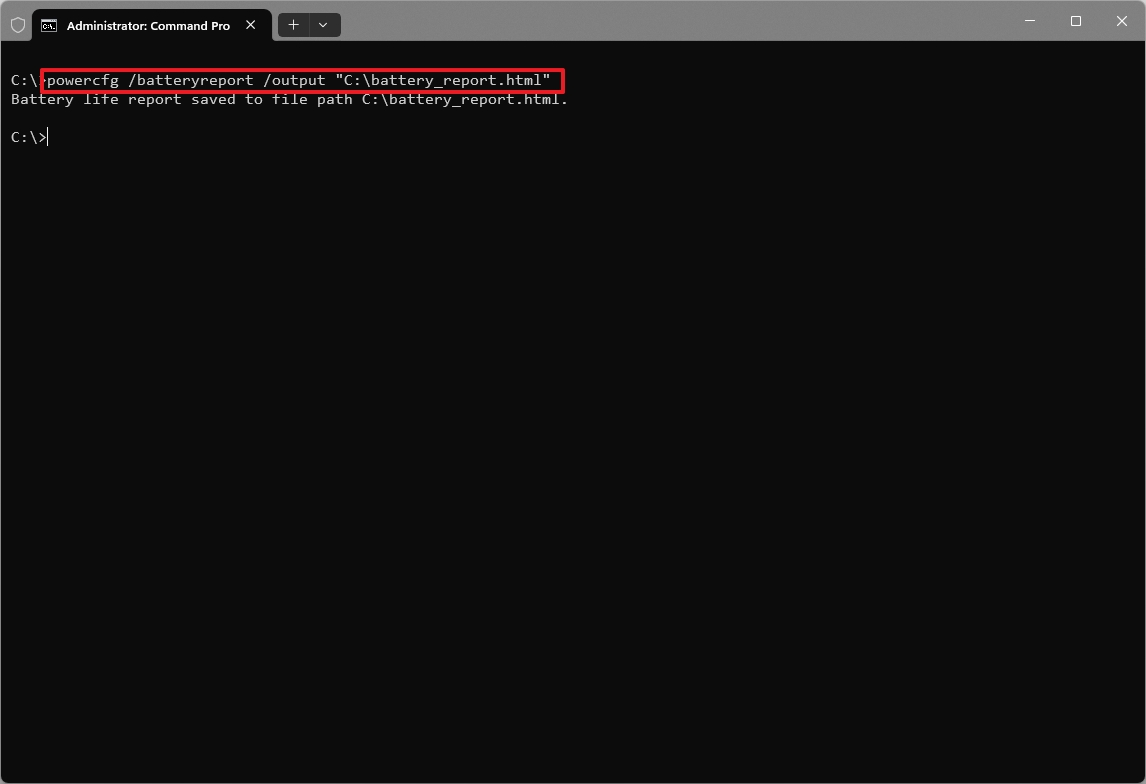
To create a report of the battery health on Windows 11, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Command Prompt, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
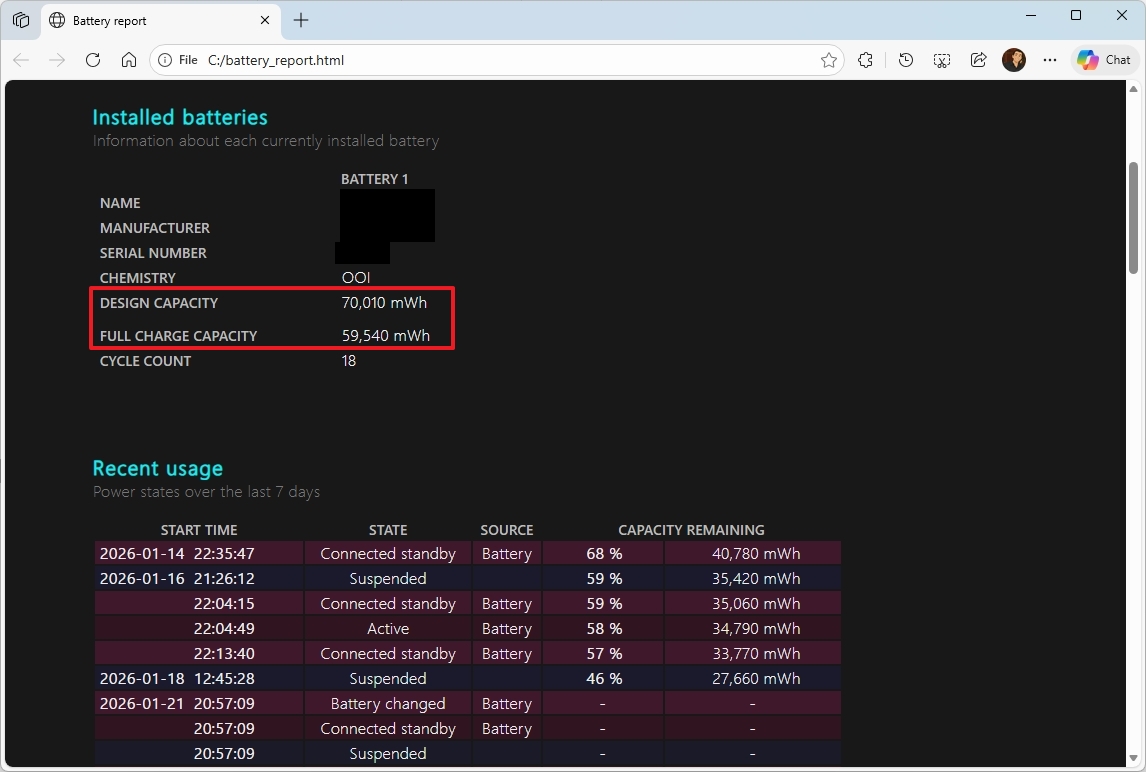
- Type the following command to create a battery report on Windows 11 and press Enter: powercfg /batteryreport /output "C:\battery_report.html"
Once you complete the steps, the command will generate and save a report in the root of the primary drive. Usually, the "C:" drive.
Open the "battery_report.html" file in the browser, and check the "design capacity" and "full charge capacity" to determine whether the battery needs replacement. If the "full charge capacity" is 50 percent or less, it's time to consider replacing the battery.
Also, sometimes, unexpected power loss can cause data corruption. On desktops, use a quality power supply or a UPS. On laptops, avoid forcing shutdowns while the system is writing data.
7. Use the right drivers to prevent hardware stress
Buggy or outdated drivers can cause crashes, freezes, and excessive processor or graphics card usage. Over a long time, this increases heat output and hardware wear, and it can even make the hardware seem due for replacement.
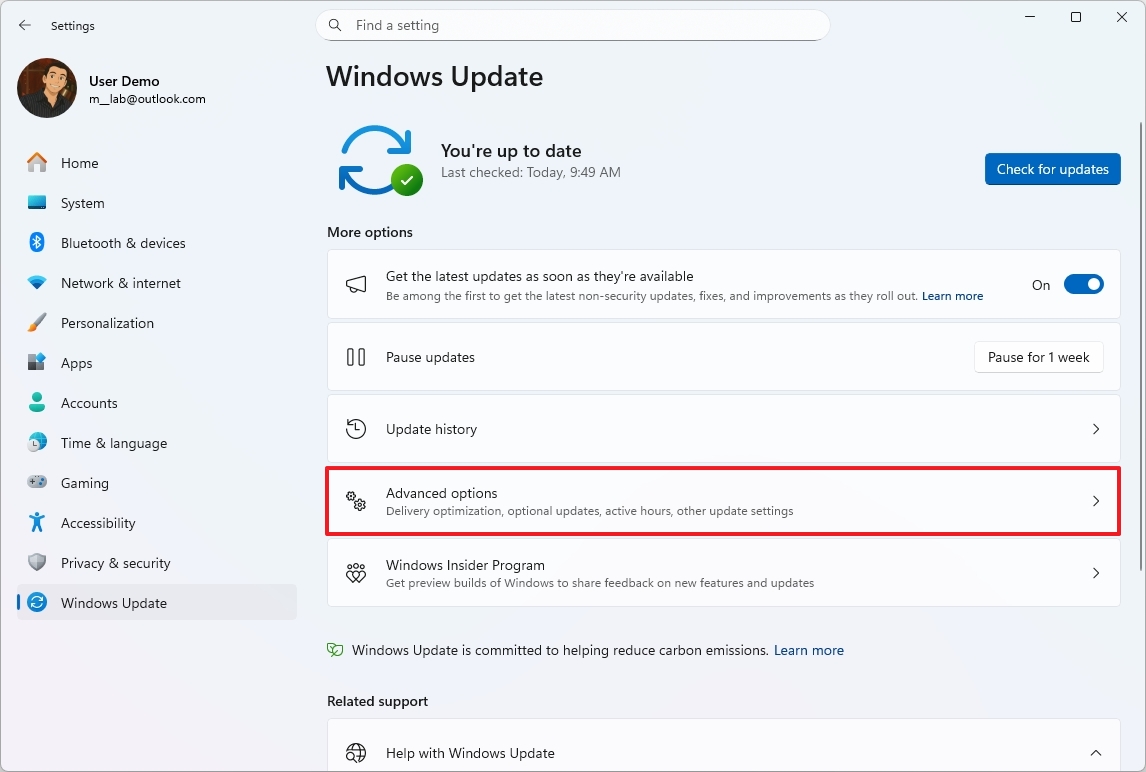
To install driver updates manually on Windows 11, use these steps:
- Open Settings.
- Click on Windows Update.
- Click the Advanced options page on the right side.
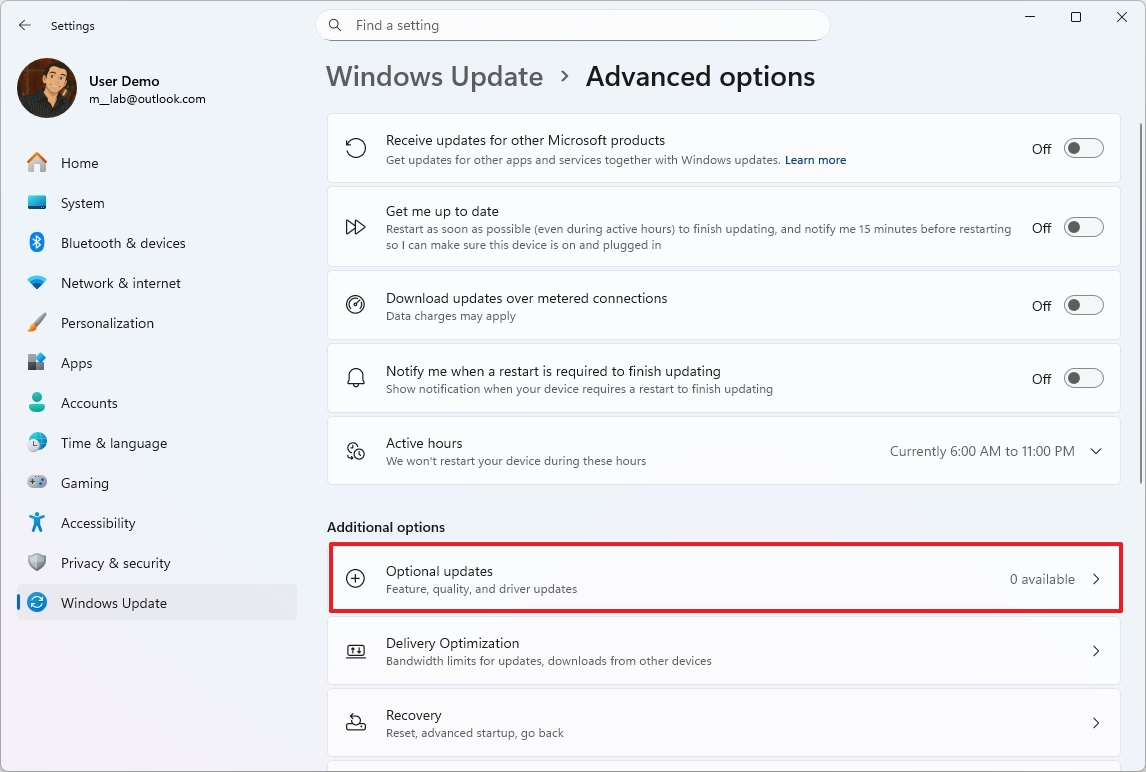
- Click the Optional updates setting under the "Additional options" section.
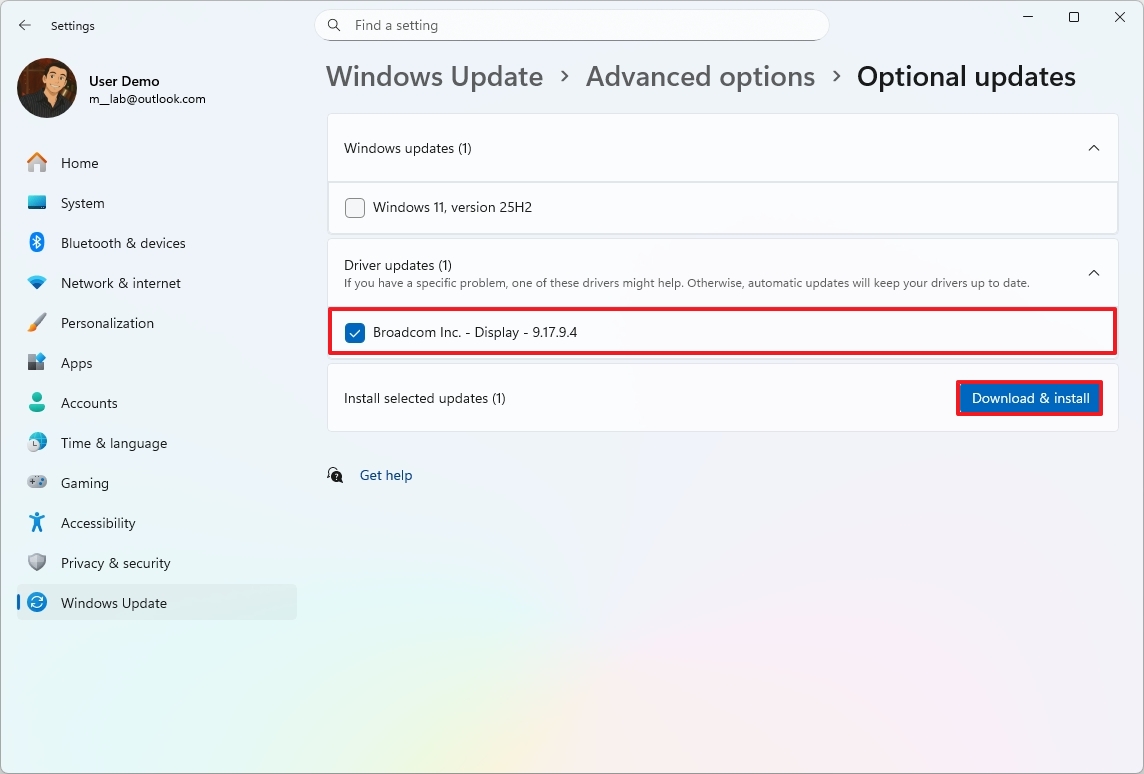
- Click the Driver updates setting.
- Check the drivers to install on your computer.
- Click the Download & install option.
Once you complete the steps, the drivers will be downloaded and installed on your computer.
You can also install device drivers in other ways, including from Device Manager and manually using your manufacturer's tool.
8. Rely on the system's security instead of heavy third-party tools
Usually, third-party antivirus suites can often consume more resources. Fortunately, Windows 11 comes with many security features that are more than adequate for any user to keep their device and data secure from malicious individuals, malware, and other online threats using fewer resources.
You can reduce system resource usage and keep your system usable longer without spending on hardware or subscriptions by using the available security features.
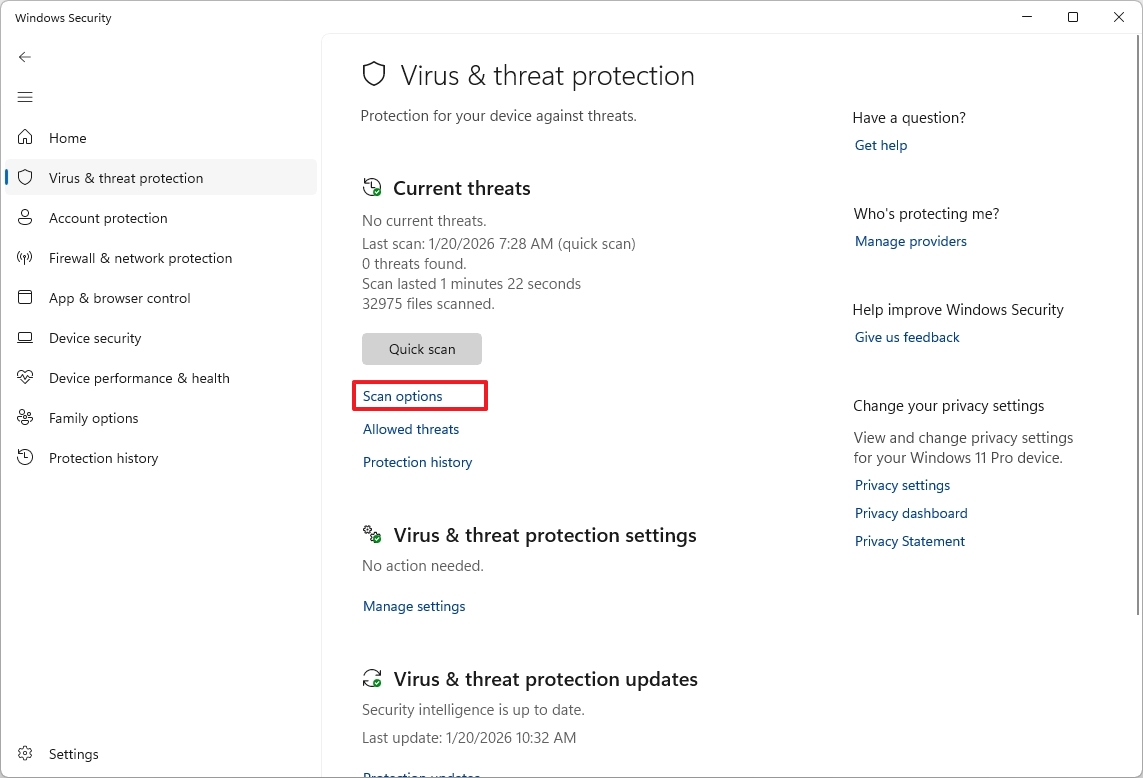
Perform a virus scan
Although the operating system proactively scans your computer for malware, you can periodically perform different types of scans.
To perform a quick scan with the Defender Antivirus, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Windows Security and click the top result to open the app.
- Click on Virus & threat protection.
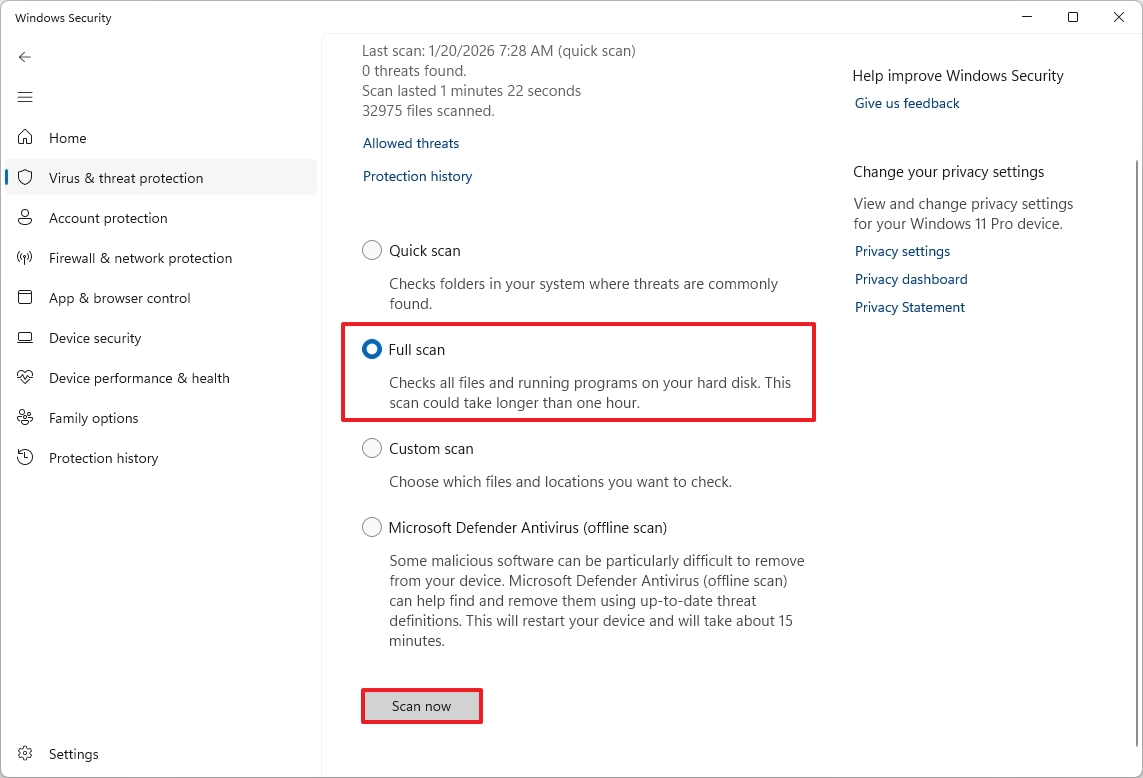
- Click the Scan options setting under the "Current threats" section.
- Select the Full Scan option.
- Click the Scan now button.
After you complete the steps, under the "Current threats" section on the main page, you can review whether the antivirus found any threats.
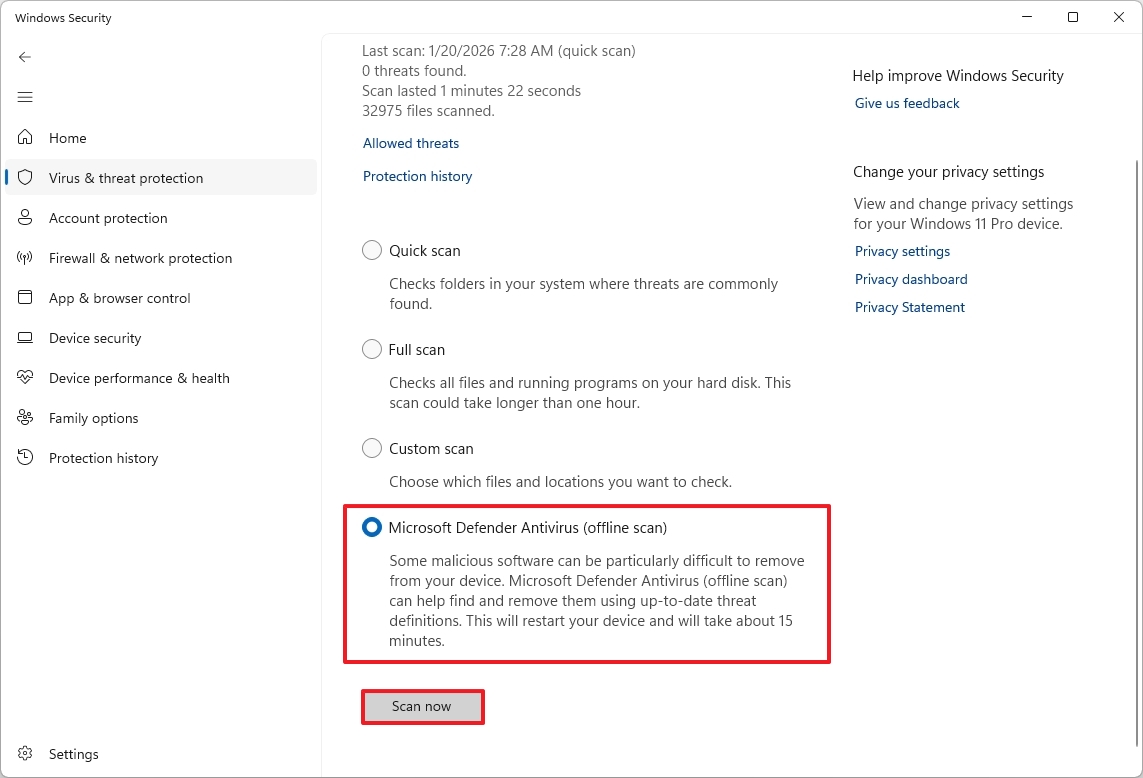
Perform an offline scan
If you encounter malware that the antivirus cannot remove while the system is running, you can try the offline option. This feature causes the computer to restart and enter the Windows Recovery Environment (WinRE) to perform a scan while the system is offline.
To perform an offline scan with the Microsoft Defender Antivirus, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Windows Security and click the top result to open the app.
- Click on Virus & threat protection.
- Click the Scan options setting under the "Current threats" section.
- Select the "Microsoft Defender Antivirus (offline scan)" option.
- Click the Scan now button.
Once you complete the steps, the antivirus's offline feature will scan the computer and automatically remove or quarantine any detected threats.
Microsoft Defender Antivirus includes many other security features and settings. You can learn more in my comprehensive guide with everything you need to know about the default antivirus on Windows 11.
Enable default system firewall
Although Microsoft Defender Firewall is enabled by default, it's always a good idea to check, enable (if applicable), and reset the settings to optimal values (unless you're actively using a custom configuration).
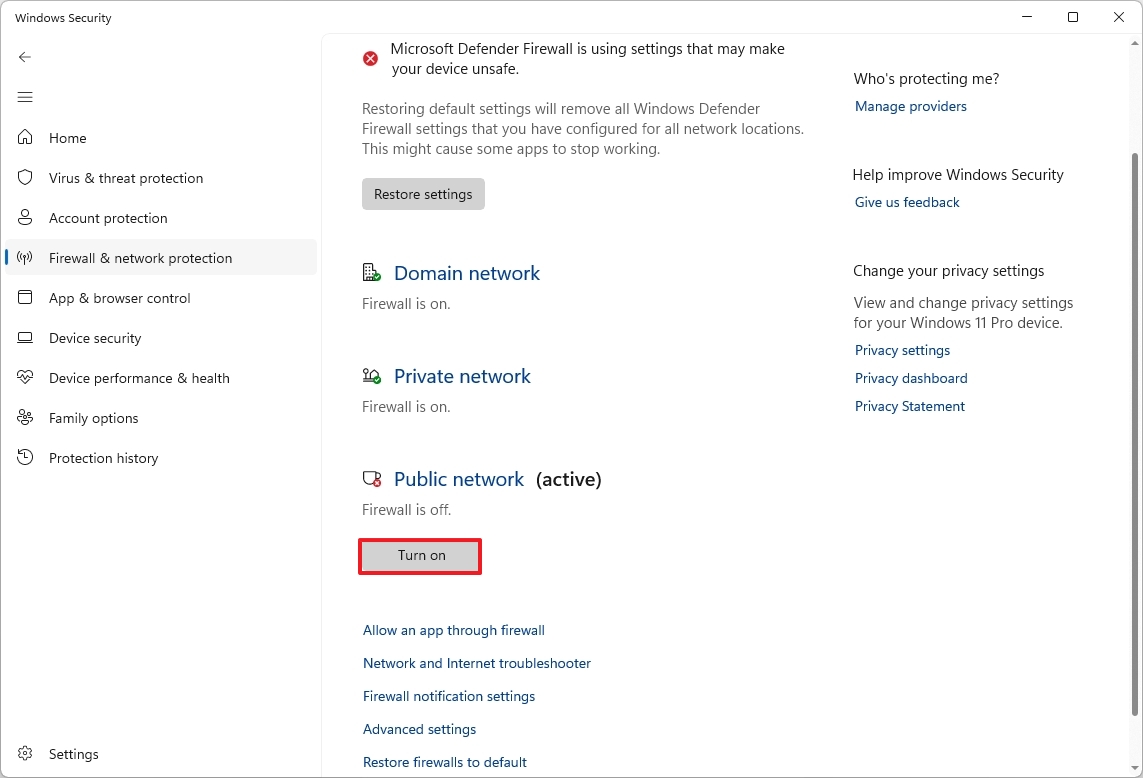
To check and enable the Defender Firewall on Windows 11, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Windows Security and click the top result to open the app.
- Click on Firewall & network protection from the left pane.
- Confirm that the network set as active has the firewall turned on.
- Click the Turn on button if the security feature is disabled.
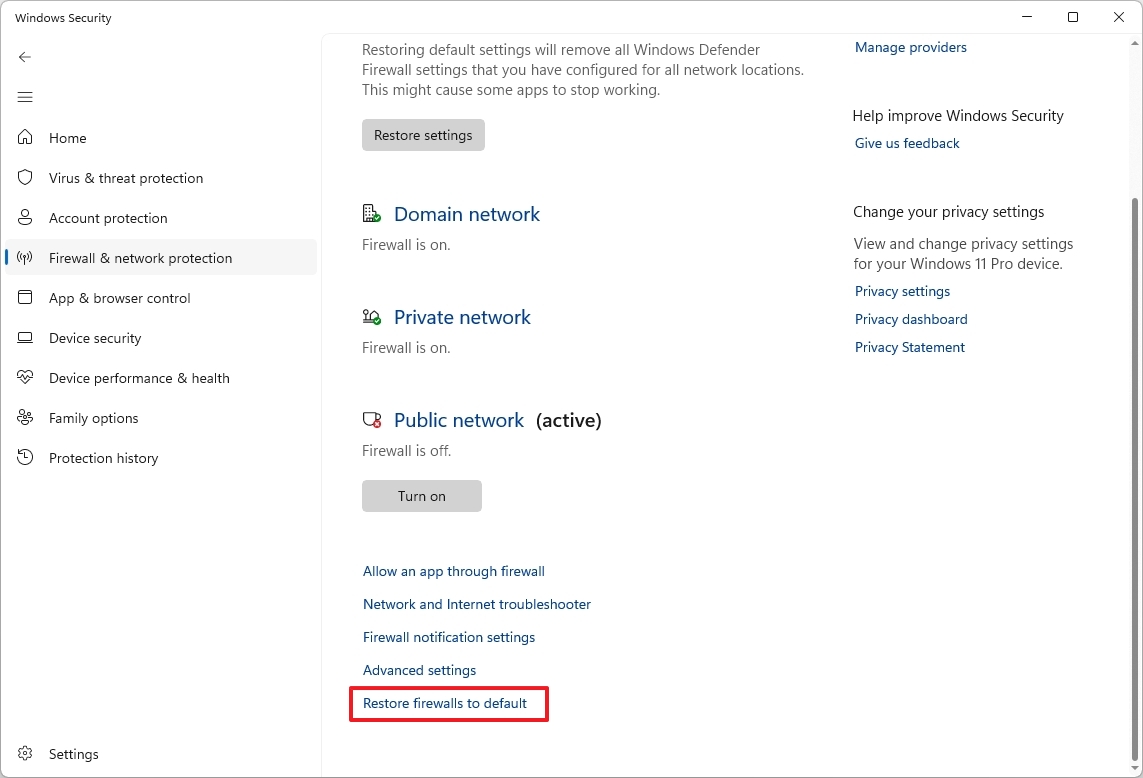
- Click the "Restore firewalls to default" option (if applicable).
- Quick tip: If you're not sure if the firewall is configured correctly, you can use these options to restore the original configuration that is optimal for most users. However, any changes you may have made will be deleted.
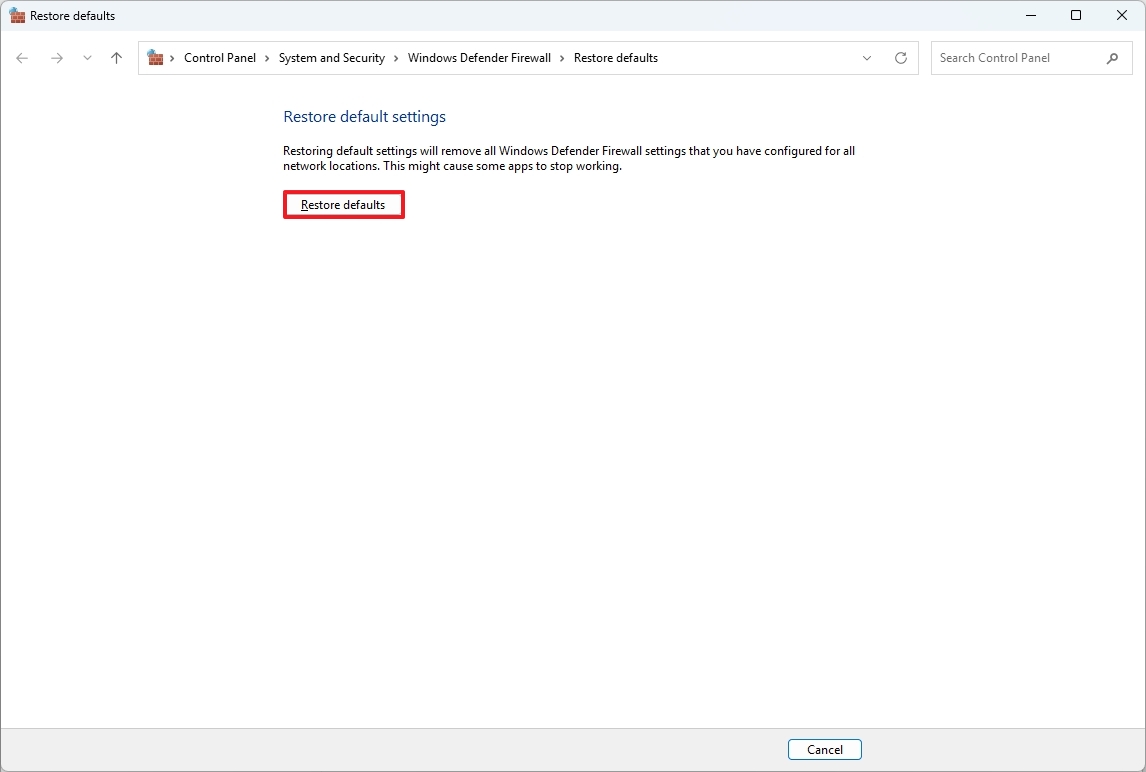
- Click the Restore defaults button.
- Click the Yes button.
Once you complete these steps, Microsoft Defender Firewall will be enabled on your computer using the recommended default configuration.
The Windows Security app also includes a suite of tools and settings to help improve the operating system's security.
9. Create regular backups to protect against unexpected failures
When storage fails or Windows 11 becomes unstable, many people replace their entire computer because they are afraid of losing their data. Regular backups remove that fear.
By using the built-in backup tools or cloud services like OneDrive, you can keep your files safe even if something goes wrong.
If you have reliable backups in place, you'll have time to fix or recover your system instead of rushing to replace it.
Create a backup on Windows 11
On Windows 11, the Backup and Restore feature lets you create a system image of your entire system, including your files, settings, apps, and the operating system. In case of a drive failure, a backup will help you to recover faster and cheaper, as you won't have to pay for data recovery.
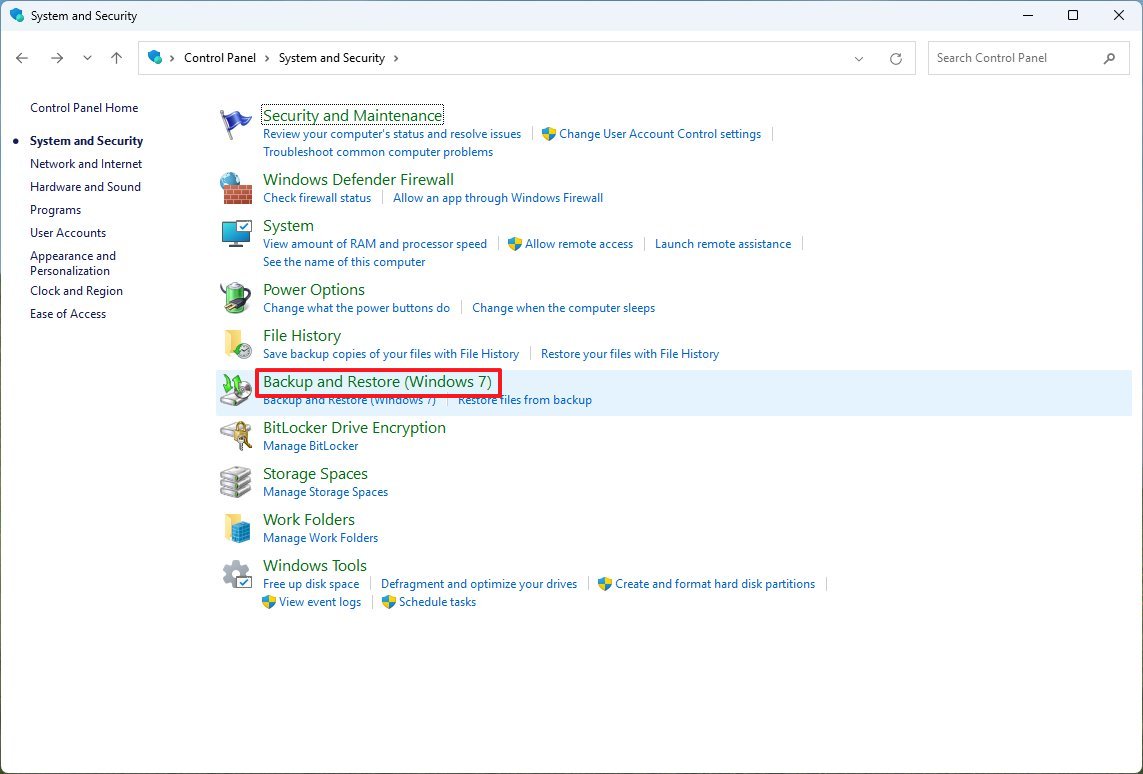
To create a full backup using the legacy Backup and Restore feature on Windows 11, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Control Panel and click the top result to open the app.
- Click on System and Security.
- Click the "Backup and Restore" setting.
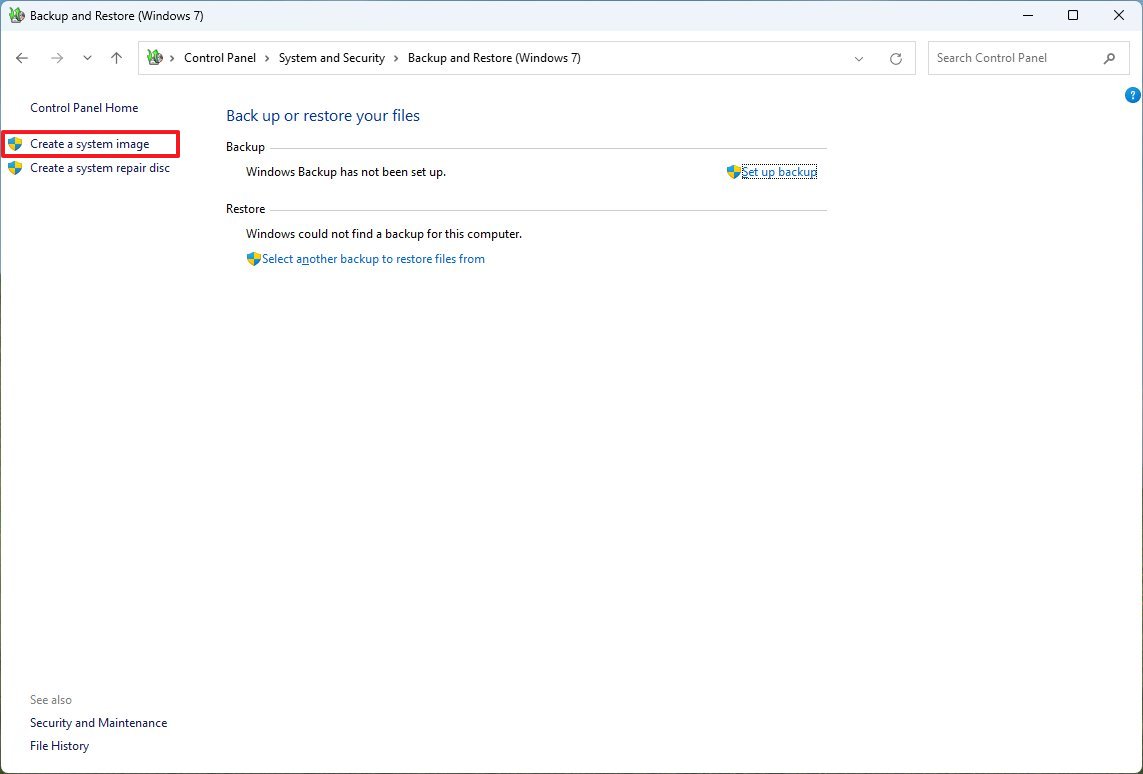
- Click the "System Image Backup" option from the bottom-left corner.
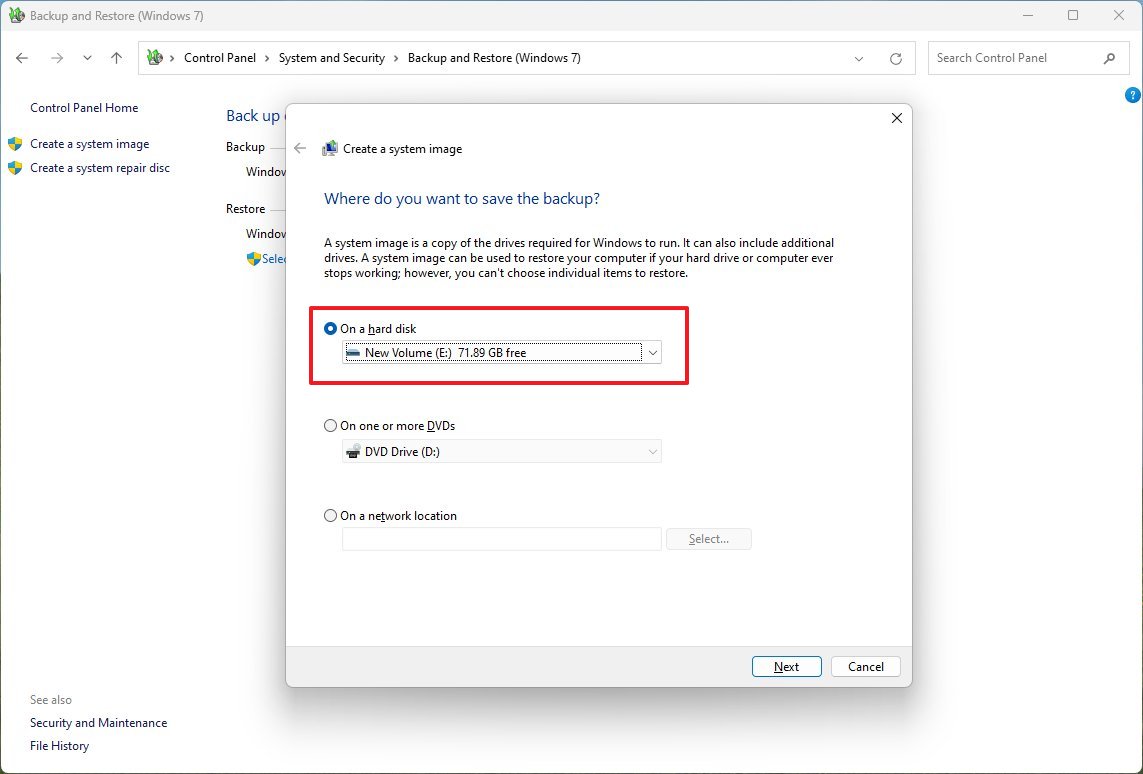
- Select the "On a hard disk" option.
- Use the "On a hard disk" drop-down menu and select the full backup destination.
- Click the Next button.
- Select any additional drives to include in the backup (if applicable).
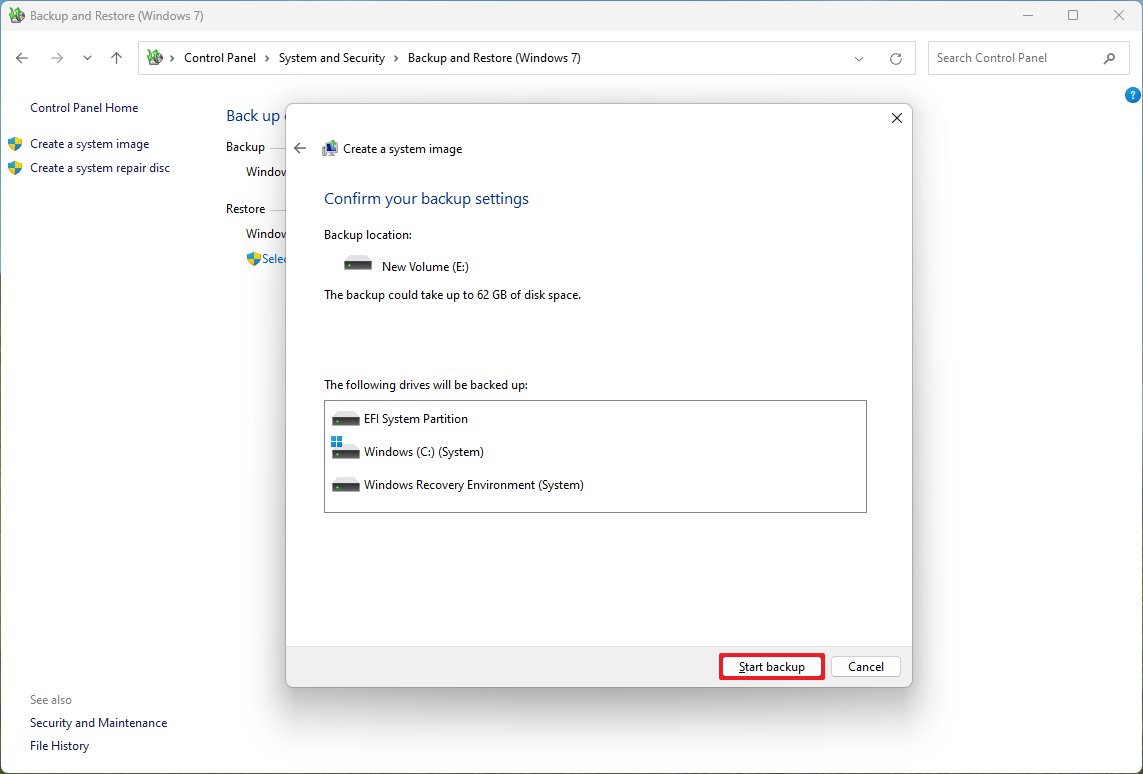
- Click the Next button.
- Click the Start backup button.
- Click the No button.
- Click the Close button.
Once you complete the steps, a backup of the entire computer will be created, including everything on the primary hard drive and any drives you may have selected.
If you need to restore your device from backup, or for additional details, you can read my instructions using the built-in backup tool on Windows 11.
10. Control heat to extend the life of expensive components
Although this guide focuses on software tweaks to extend your computer's lifespan, basic hardware maintenance is equally important. Dust buildup and poor airflow can cause throttling and long-term degradation, so keeping vents clear and ensuring proper airflow is essential.
Even though some modern laptops are fanless, many devices still have fans and vents. If your laptop has them, it's important to check and clean these components regularly to maintain proper airflow and prevent overheating.
Desktop users should also clean vents and dust filters periodically (if applicable). Installing additional case fans or upgrading the cooling system can help lower overall temperatures, reducing wear on components.
Pay attention to fan noise, as louder operation may indicate worn bearings that need replacement. While opinions vary, replacing the processor's thermal paste every 5 years (or so) if thermal problems arise can also help keep temperatures lower. Excessive heat can shorten the lifespan of processors, graphics cards, and drives, all of which are (now) costly to replace.
With memory and storage prices rising and new computers becoming more expensive, extending the life of your current system is as much a financial strategy as a technical one. Windows 11 provides the tools to help manage and maintain your device. Using them consistently can delay costly upgrades, reduce component wear, and keep your system performing reliably for years.
FAQs about performing maintenance on Windows 11
These are common questions regarding the steps to maintain a computer running Windows 11.
Does regular maintenance really extend the life of a Windows 11 PC?
Yes. Consistent software and hardware maintenance reduces unnecessary wear on components, prevents performance degradation, and minimizes failures that often lead users to replace otherwise functional hardware.
Can high memory usage make a PC feel older than it is?
Excessive RAM usage from startup apps, background services, or malware can cause slowdowns that mimic aging hardware, even on relatively new systems.
How often should I clean up storage on Windows 11?
You should review storage usage at least once a month. Running out of free space can cause failed updates, slower performance, and increased SSD wear.
Is it safe to use third-party cleanup and optimization tools?
In most cases, no. Aggressive cleanup tools can remove required system files or Registry entries, leading to instability and forced reinstalls. Windows 11’s built-in storage and maintenance tools are safer and more than enough.
Does Windows 11 automatically take care of SSD maintenance?
Yes, Windows 11 automatically manages SSDs using TRIM and optimization tasks. However, users should still monitor free space, temperatures, and drive health to avoid premature failure.
Can battery habits really affect a laptop’s lifespan?
Yes. Frequently charging to 100 percent, deep discharges, and excessive heat accelerate battery degradation. Using charging limits and avoiding full discharges can significantly extend battery life.
Is Microsoft Defender enough to protect Windows 11 long term?
For most users, yes. Microsoft Defender provides strong real-time protection with lower system impact than many third-party antivirus suites, helping preserve performance and hardware longevity.
More resources
Explore more in-depth how-to guides, troubleshooting advice, and essential tips to get the most out of Windows 11 and 10. Start browsing here:
- Windows 11 on Windows Central — All you need to know
- Windows 10 on Windows Central — All you need to know

Follow Windows Central on Google News to keep our latest news, insights, and features at the top of your feeds!

Mauro Huculak has been a Windows How-To Expert contributor for WindowsCentral.com for nearly a decade and has over 22 years of combined experience in IT and technical writing. He holds various professional certifications from Microsoft, Cisco, VMware, and CompTIA and has been recognized as a Microsoft MVP for many years.
You must confirm your public display name before commenting
Please logout and then login again, you will then be prompted to enter your display name.